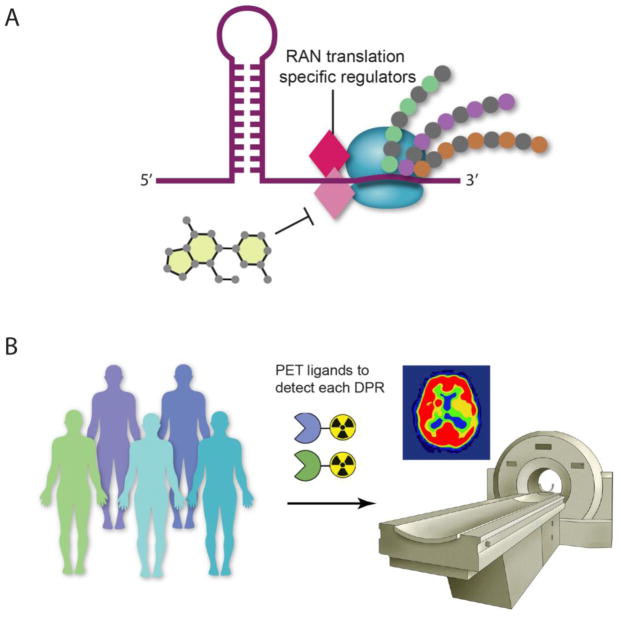
Figure 4. Additional experiments to test C9orf72 dipeptide repeat protein toxicity.
A) To specifically block RAN translation will require elucidating RAN translation mechanisms and identifying RAN translation-specific regulators. These putative regulators will be new targets for the development of small molecule inhibitors to specifically inhibit RAN translation. B) The development of positron emission tomography (PET) ligands to detect DPR pathology in vivo would allow longitudinal studies of C9orf72 mutation carriers to help resolve the role of DPRs in disease pathogenesis and to eventually be used in clinical trial settings to assess efficacy of candidate therapeutics.