Figure 3. Anti-NC16A IgG4 inhibit binding and C.
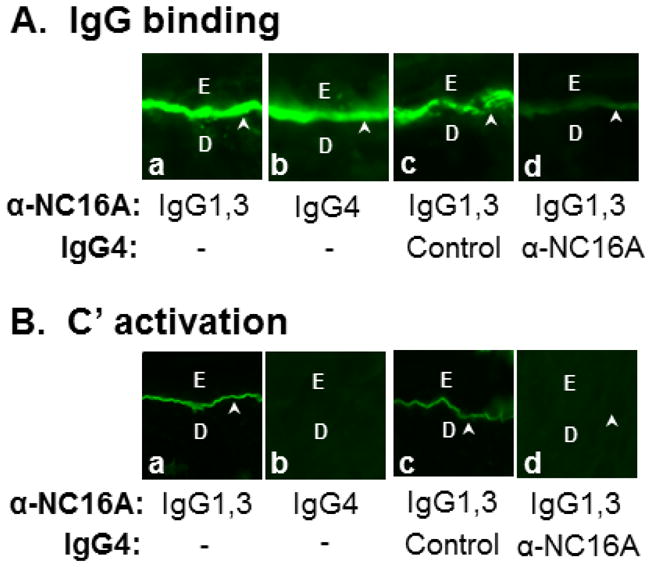
′ fixation of anti-NC16A IgG1,3 at the BMZ in vitro.
Skin sections of NC16A mice were incubated with anti-NC16A IgG1,3 (1 μg/ml), IgG4 (0.25 μg/ml), or both IgG1,3 and IgG4 in the absence or presence of freshly prepared human serum (providing complete complement system). A. IgG binding. Anti-NC16A igG1,3, and 4 stained the BMZ. Pre- or co-incubation of anti-NC16A IgG4 but not control IgG4 with anti-NC16A IgG1,3 drastically reduced binding of anti-NC16A IgG1,3 at the BMZ as detected by FITC-conjugated IgG1-spefici secondary antibody (panel d). B. C′ fixation. In the presence of human serum, anti-NC16A IgG1,3 and not IgG4 fixed complement as determined by C3 deposition at the BMZ using FITC-conjugated human C3-specific secondary antibody. Pre- or co-incubation of anti-NC16A IgG4 but not control IgG4 with anti-NC16A IgG1,3 significantly inhibited C′ fixation by anti-NC16A IgG1,3 (panel d).
