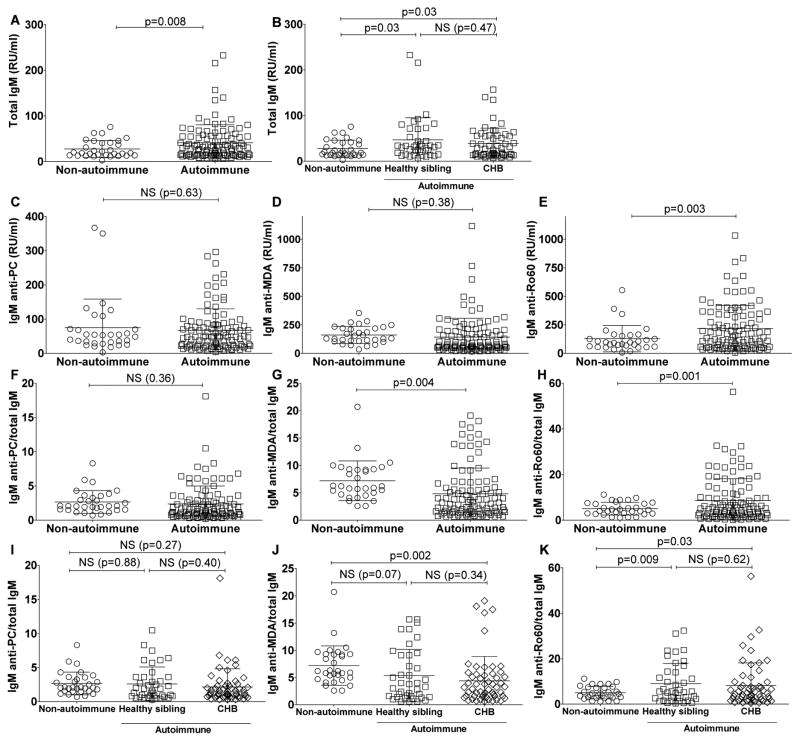
Figure 5. IgM levels in cord blood from control newborns compared to newborns with autoimmune mothers.
IgM levels were measured in 31 control cord bloods (from non-autoimmune mothers) and 103 cord blood samples from the NL registry from newborns with autoimmune anti-Ro60/52/La positive mothers (autoimmune). Within the autoimmune cohort 56 samples came from neonates with congenital heart block (CHB) and 40 from clinically healthy siblings. A. Total IgM levels. B. Total IgM levels for autoimmune neonates with or without heart block. C. IgM anti-PC levels. D. IgM anti-MDA levels. E. IgM anti-Ro60 levels. F. The ratio of IgM anti-PC/total IgM. G. The ratio of IgM anti-MDA/total IgM. H. The ratio of IgM anti-Ro60/total IgM. I. The ratio of IgM anti-PC/total IgM for neonates, from autoimmune mothers, with or without heart block. J. The ratio of IgM anti-MDA/total IgM for neonates, from autoimmune mothers, with or without heart block. K. The ratio of IgM anti-Ro60/total IgM for neonates from autoimmune mothers, with or without heart block. Binding assays were performed by ELISA. P-values were derived from 2-sided unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction.