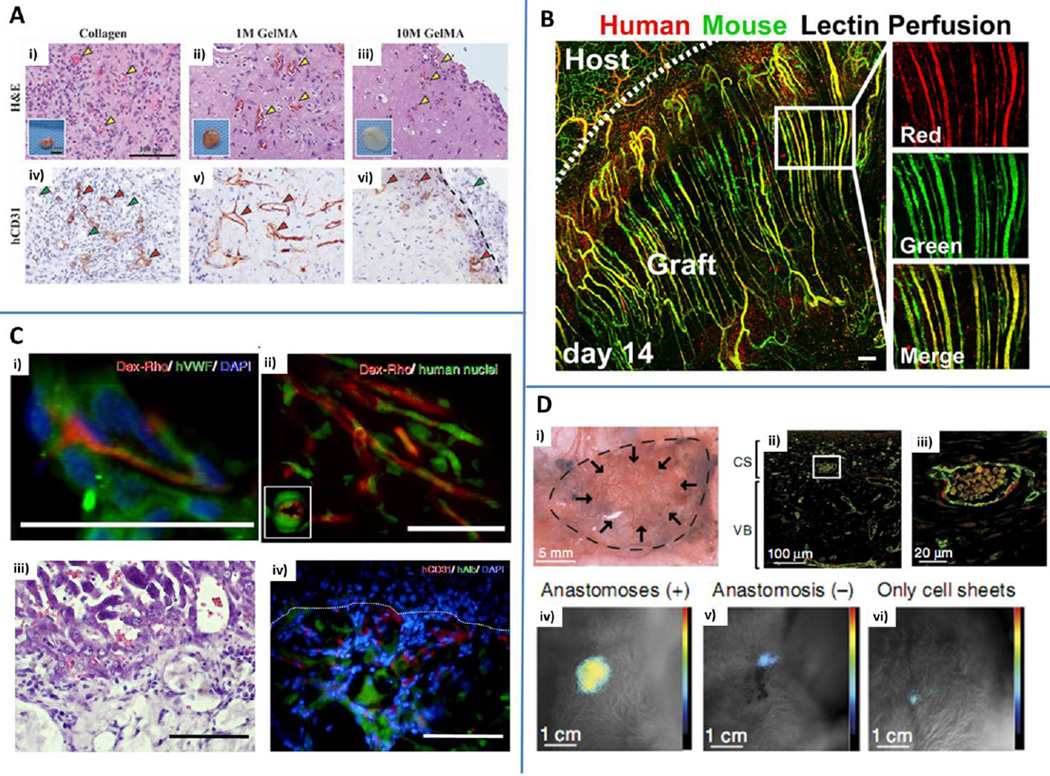
Fig. 8.
In vivo applications. A) 1M and 10 M GelMA hydrogels with embedded human endothelial colony forming cells and mesenchymal stem cells were in vitro pre-cultured for 24 h and implanted in mice. Collagen gels were used as controls. Hematoxylin&eosin (H&E) staining revealed the presence of blood vessels containing mouse erythrocytes (yellow arrowheads) within collagen (i), 1M GelMA (ii) and 10 M GelMA (iii). Explants are shown in the insets. Human CD31 staining (iv, v, vi) highlights the presence of human capillaries (red arrowheads) while murine vessels are not stained (green arrowheads). Reproduced from Chen et al. (2012) by permission of John Wiley and Sons. B) Parallel arrays of EC cords anastomosed with the mouse vasculature. Human-specific lectin (red) and mouse-specific lectin (green) were infused via tail vein injection demonstrating the presence of patent vessels chimeric in composition. Scale bar: 150 µm. Reproduced by permission from Baranski JD, Chaturvedi RR, Stevens KR, Eyckmans J, Carvalho B, Solorzano RD, et al. Geometric control of vascular networks to enhance engineered tissue integration and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:7586-91 (Baranski et al. (2013)). C) Hydrogels obtained with interfacial polyelectrolyte complexation anastomosed with the host vasculature after 14 days, as demonstrated by dextran rhodamine (Dex-Rho) injection (i and ii, red). Green: human vWF (i) and human nuclei (ii). H&E (iii) and immunofluorescent staining (iv) of hepatocyte constructs. Human serum albumin (hAlb, green) and human CD31 (red) were identified within tissue constructs. Scale bar: 50 µm (i and ii) and 100 µm (iii and iv). Blue: nuclei (DAPI). Adapted from Figure 2 and Figure 4 (Leong et al. (2013)) by permission of the Nature Publishing Group. D) Vascularized grafts obtained by cell sheet engineering anastomosed with the host circulatory system and maintained their functionality for at least 14 days following implantation (i). Immunofluorescence staining of CD31 (green) and calponin (red) showing uniform distribution of vessels inside the tissue construct. CS: cell sheets. VB: vascular bed (ii and iii (enlargement)). Bioluminescent image representative of the integration of the tissue construct with the host. Higher signals were detected for anastomosed tissues (iv) compared to non-anastomosed (v) or constructs embedding cell sheets without a connecting vascular bed (vi). Reproduced from Sekine et al. (2013) by permission of the Nature Publishing Group.