Figure 1.
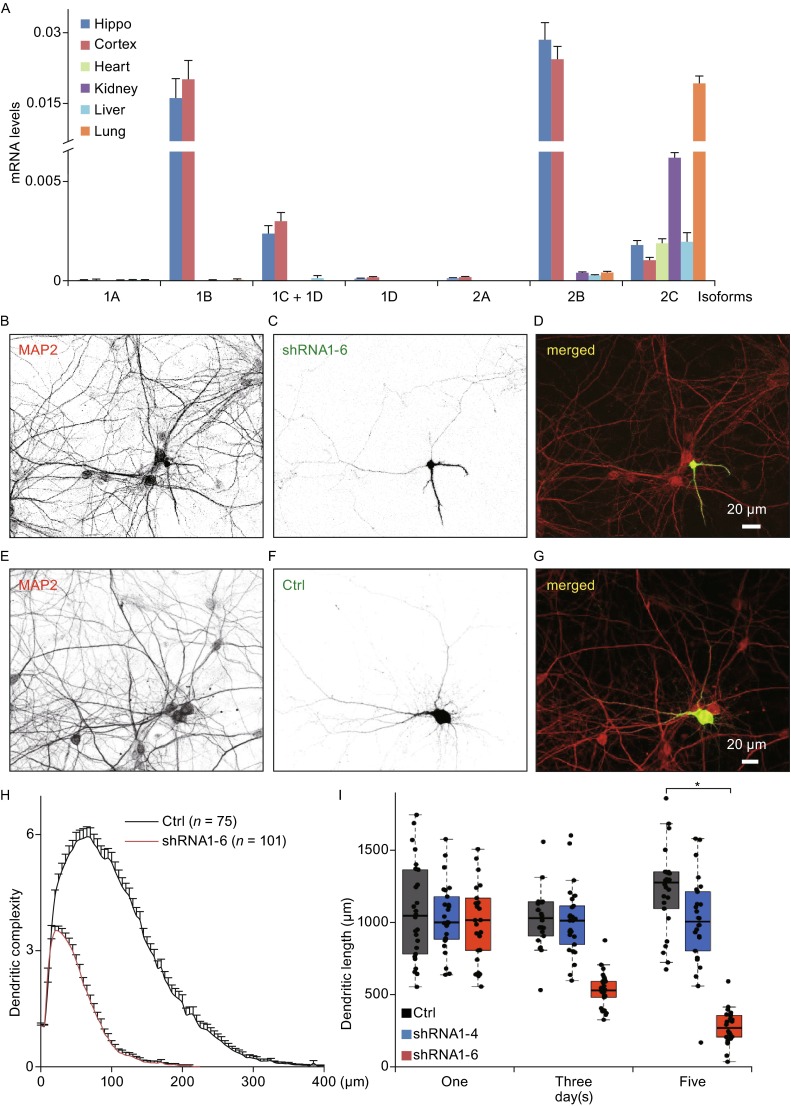
Knockdown of cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 1 ( Dync1i1 ) causes dendritic atrophy in primary hippocampal neurons. (A) The quantitative-PCR results show the expression levels of cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chains, including the isoforms of Dync1i1 (1A, 1B, 1C, and 1D) and the isoforms of Dync1i2 (2A, 2B, and 2C) in P0 rat hippocampus, cortex, heart, kidney, liver, and lung tissues. (B–G) Representative neurons are transfected with shRNA1-6 (B–D, a specific shRNA of Dync1i1, see also Fig. S1) or Ctrl (E–G) at DIV6 and immunostained for the dendritic marker MAP2 (red in D and G) at DIV11. Green neurons are shRNA1-6 or Ctrl transfected neurons (green in D and G). The scale bars represent 20 μm. (H) Sholl analysis for dendritic complexity of neurons transfected with control vector (Ctrl, n = 75) and Dync1i1 shRNA1-6 (n = 101). In control neurons, the maximum length of dendrite branches is found between 300 and 400 µm from the cell body. The shRNA1-6 transfected neurons show marked shortened dendrites such that the majority of dendrites were located within 200 µm of the soma. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. (I) Scatterplots with boxplots show that knockdown of DYNC1I1 expression causes dendritic atrophy. Primary hippocampal neurons are transfected with control vector (Ctrl, n = 26, gray box), control shRNA (shRNA1-4, n = 26, blue box) or shRNA1-6 (n = 26, red box) of Dync1i1 at DIV6. Following transfection, neurons are cultured additional 1, 3 or 5 days before imaging and quantification of total dendritic length. The total dendritic lengths of control neurons slightly increase with increasing days in vitro. There is almost no length change of shRNA1-4 transfected neurons. However, the total dendritic lengths of shRNA1-6 transfected neurons are gradually and dramatically reduced at 3 and 5 days after transfection. *, P < 0.001
