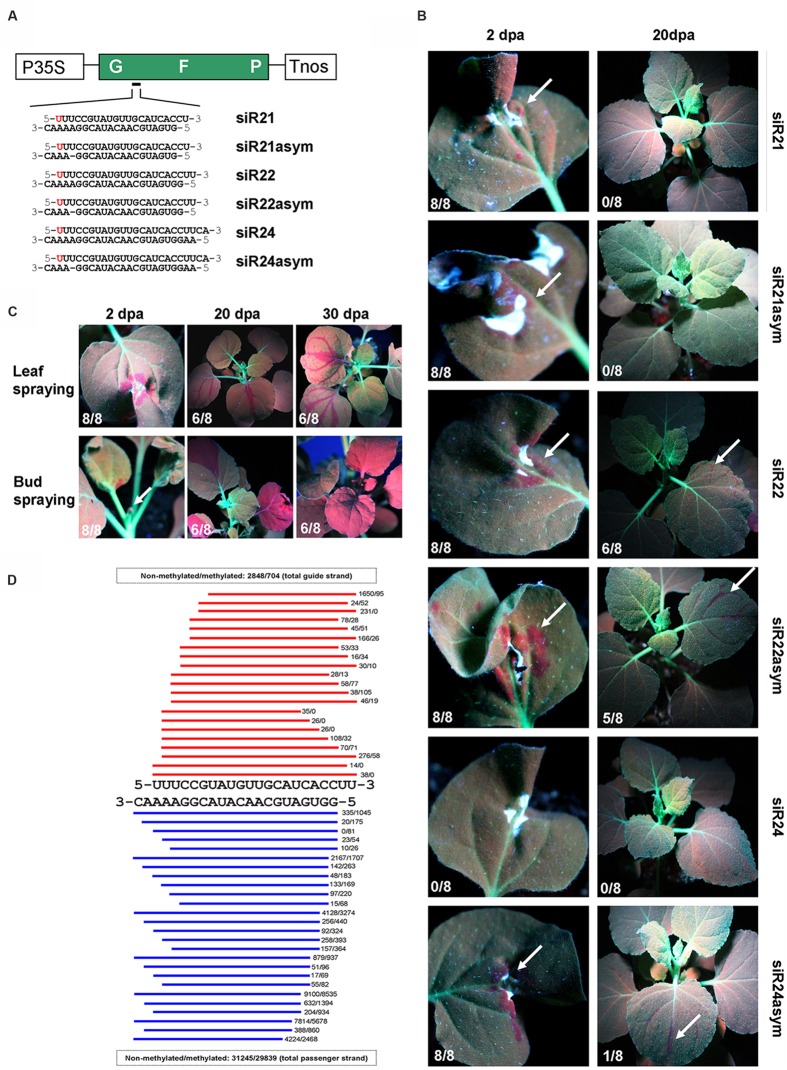
FIGURE 1.
High-pressure spraying of GFP siRNAs into Nb-16C plants. (A) Schematic representation of the GFP transgene. P35S: 35S promoter of the Cauliflower mosaic virus, GFP: GREEN FLUORESCENT PROTEIN cDNA; Tnos: nopaline synthase terminator. The sequences of 21-, 22-, and 24-nt GFP siRNAs, containing or not containing an asymmetric bulge (‘asym’) are indicated. For all siRNAs, the guide strand starts with 5′-U, indicated in red. (B) Monitoring of Nb-16C plants under UV-light 2 and 20 days post application (dpa) of siRNAs by high-pressure spraying, respectively. White arrows indicate regions of silencing. For each experiment eight plants were tested, and the number of silenced plants (X/8) is indicated at the bottom left of each image. (C) Monitoring of Nb-16C plants under UV-light 2, 20, and 30 dpa of siR22 by high-pressure spraying, respectively. Spraying was either targeted at the leaf or the bud. White arrows indicate regions of silencing. For each experiment eight plants were tested, and the number of silenced plants (X/8) is indicated at the bottom left of each image. (D) Small RNA deep sequencing of Nb-WT plants 2 dpa of methylated and non-methylated siR22 by high-pressure spraying. Red and blue bars represent guide and passenger strands, respectively. The total number of siRNA reads is indicated.