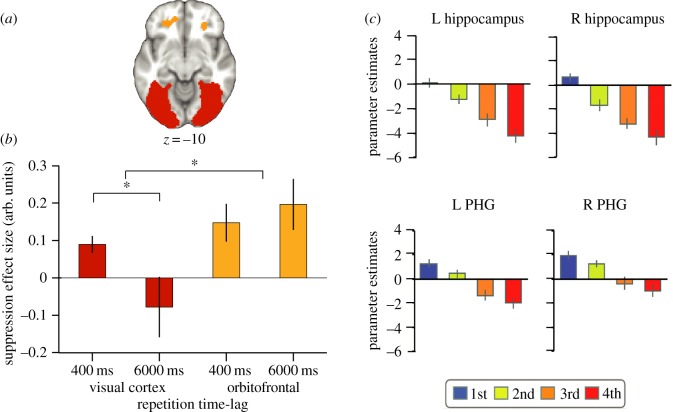
Figure 6.
Reptition time-lag and exposure: factors to consider when designing an fMRI repetition suppression experiment. (a) regions of interest in the visual cortex and orbitofrontal cortex from which repetition suppression was measured, adapted from [145]. (b) An interaction was observed between the brain regions shown in (a) and the time-lag across which repetition suppression was observed. In both the visual cortex and OFC, suppression was observed if a stimulus was repeated after 400 ms. However, only the OFC showed repetition suppression if a stimulus was repeated after 6000 ms, suggesting a difference between anterior and posterior brain regions, adapted from [145]. (c) Repetition suppression in the left (L) and right (R) hippocampus and the parahippocampal gyrus (PHG) declines linearly as a function of the number of presentations or repetitions of a stimulus, adapted from [147].