Figure 1.
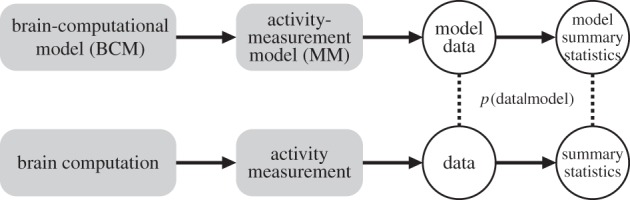
Evaluating a brain-computational model with brain-activity measurements. To evaluate each of a number of competing BCMs, we would like to compute the likelihood p(data|model) for each model. We need to account not only for the brain computations (using a BCM) but also for the measurement process (using an MM). The MM simulates the way the measurement channels sample the units of the BCM. One approach to inference is to evaluate the likelihood at the level of the measurements. This requires fitting a parametrized MM to predict each individual measurement channel. To avoid having to fit an MM to each channel, we instead predict summary statistics of the population of possible measurement channels.
