Fig. 7.
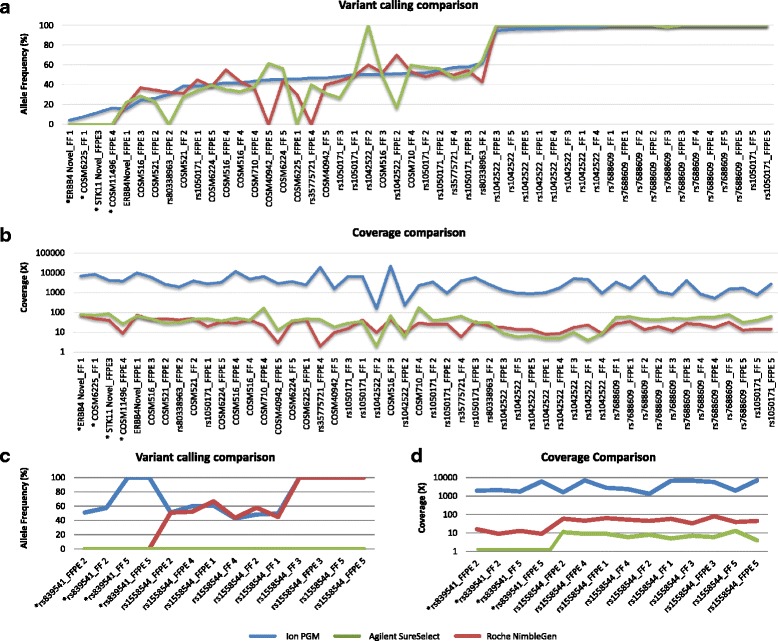
Variant calling comparison between Ion PGM data and both WES systems. Variant calling comparison between Ion PGM data (blue) and both Agilent SureSelect (green) and Roche NimbleGen (red) data in exon regions shows 88 % of concordance (44/50) in both WES capture systems (a). Both systems failed to call 4 genetic variants (*) detected by Ion PGM platform at low frequencies (4-16 %). Further 4 variants were missed as follows: 2 by Agilent (COSM6225, rs80338963) and 2 by Roche NimbleGen (COSM40942, rs35775721). Horizontal axis reports the genetic variants (Additional file 3: Table S8a) ordered from lowest to highest frequency (vertical axis) as assessed by Ion PGM platform. Variant coverage displays a quite similar trend between Agilent (green) and Roche NimbleGen (red) libraries, and is far lower than Ion PGM platform (blue) (b). Two Roche libraries report a low coverage in the uncalled variants (COSM40942, rs35775721). Vertical axis displays the variant coverage in logarithmic scale. Variant calling comparison between Ion PGM data (blue) and both Agilent (green) and Roche NimbleGen (red) data in non-exon regions shows a poor performance of both WES technologies (c). Both WES systems failed to call the rs839541 (*) SNP in ERBB4 gene, whereas rs1558544 SNP in EGFR was missed by all 10 Agilent libraries. Vertical axis reports the frequency of the genetic variants. Variant coverage comparison between Ion PGM data (blue) and both Agilent (green) and Roche NimbleGen (red) data in non-exon (intron/downstream/upstream) regions reports a low coverage in both exome capture kits (d); rs839541 SNP was completely uncovered in Agilent libraries. Vertical axis displays coverage values in logarithmic scale
