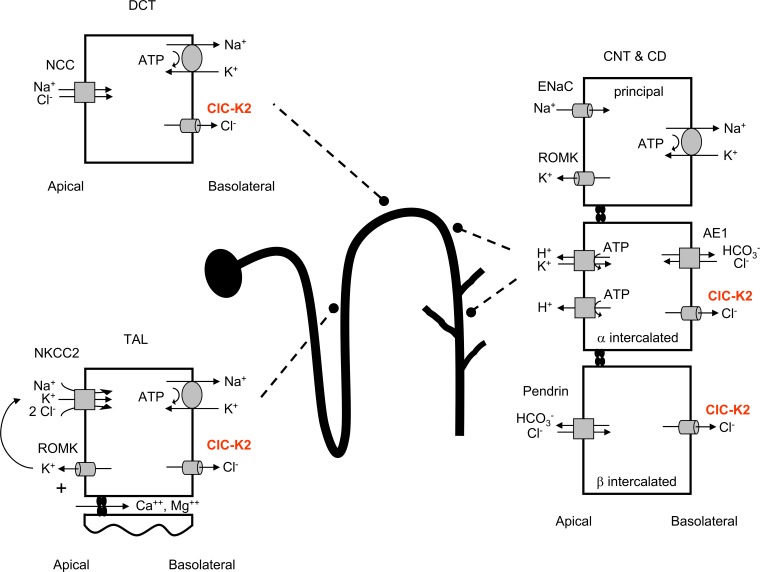
Figure 1.
The metabolic alkalosis of Bartter’s syndrome can arise from an increase in acid secretion from α intercalated cells and a decrease in base secretion from β intercalated cells. Depiction of the renal nephron showing the cells and transporters involved in the renal salt wasting and alkalosis of Bartter’s syndrome. CD, collecting duct; CNT, connecting tubule; DCT, distal convoluted tubule; NCC, sodium chloride cotransporter; ROMK, renal outer medullary potassium channel; TAL, thick ascending limb.