Figure 2.
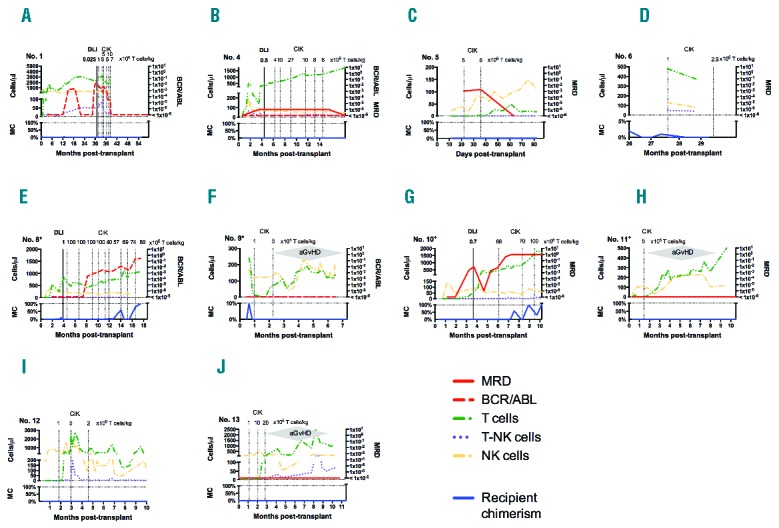
Immune reconstitution. After cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cell treatment patients were sequentially screened for relapse, for occurrence of acute graft-versus-host-disease (aGvHD) and for T, natural killer (NK), and T-NK cell counts. Patients with treatment responses for whom immune monitoring data were available are shown. Immune monitoring demonstrated that T-cell numbers, followed by NK and to a lesser extent T-NK cell counts constantly increased after receiving more than 1×106 CD3+CD56− CIK cells/kg, which correlated with appearance of aGvHD especially in the haploidentical transplantation setting (F, H, J). In most cases T-cell counts slightly decreased 2–4 weeks after infusions, but increased thereafter above levels before infusion. During increase of immune effector cells, short-term anti-leukemic effects were observed in the matched transplantation setting (B, D, E, G) whereas in the haploidentical setting (A, C, F, H, I, J), increase of immune cells resulted in clearance of minimal residual disease (MRD) and BCR-ABL/ABL or conversion to full donor chimerism.
