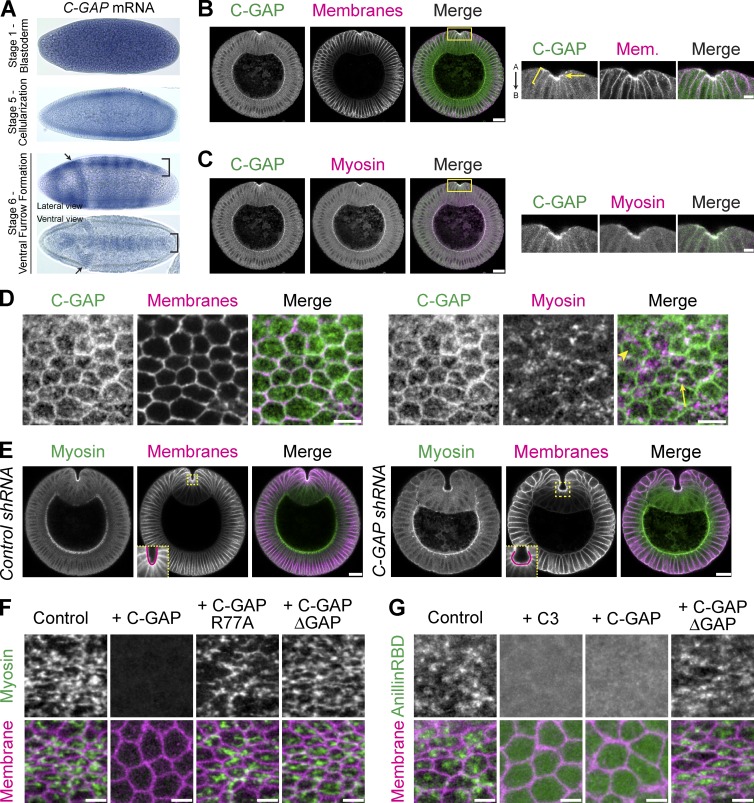
Figure 3.
Identification of a RhoA GAP, Cumberland GAP, involved in tissue folding. (A) In situs of C-GAP mRNA. C-GAP mRNA is maternally loaded and enriched in ventral (bracket) and cephalic (arrows) furrows. (B and C) C-GAP is apically enriched (arrow) in the ventral furrow, and localizes along subapical/basolateral membranes (brackets). Images from fixed embryo, cross sections stained for C-GAP::3xHA (HA epitope), and membranes (neurotactin) or myosin (zipper). Images on right represent magnified regions from images on left (yellow boxed regions). "A" is apical and "B" is basal. (D) C-GAP localizes across the apical surface. Images from fixed myosin::GFP (sqh::GFP) embryos, stained for C-GAP::3xHA (HA) and with phalloidin (subapical F-actin, membranes). C-GAP forms medioapical structures with (arrow) and without (arrowhead) myosin. (E) Images from fixed Control (white) and C-GAP shRNA cross sectioned embryos, stained for myosin (zipper) and membranes (neurotactin). Ventral furrow in Control forms in a V-shape, but C-GAP shRNA ventral furrow is abnormally shaped, forming a cup, or C-shape (insets at bottom left of membrane channel are from boxed, yellow region). (F) C-GAP overexpression decreases apical myosin accumulation. Images from live embryos expressing myosin::GFP and membrane::RFP, injected with mRNA encoding full-length C-GAP, C-GAP with GAP mutant (R77A), C-GAP with GAP domain deletion, or control (water injection). (G) C-GAP overexpression decreases apical RhoA-GTP. Images from live embryos expressing Rho-GTP biosensor (AniRBD::GFP) and membrane::RFP and injected with PBS buffer (control), C3, or mRNA encoding full-length C-GAP or C-GAP with a GAP domain deletion. Bars: (B and C [right], D, F, and G) 5 µm; (B and C [left] and E) 20 µm.