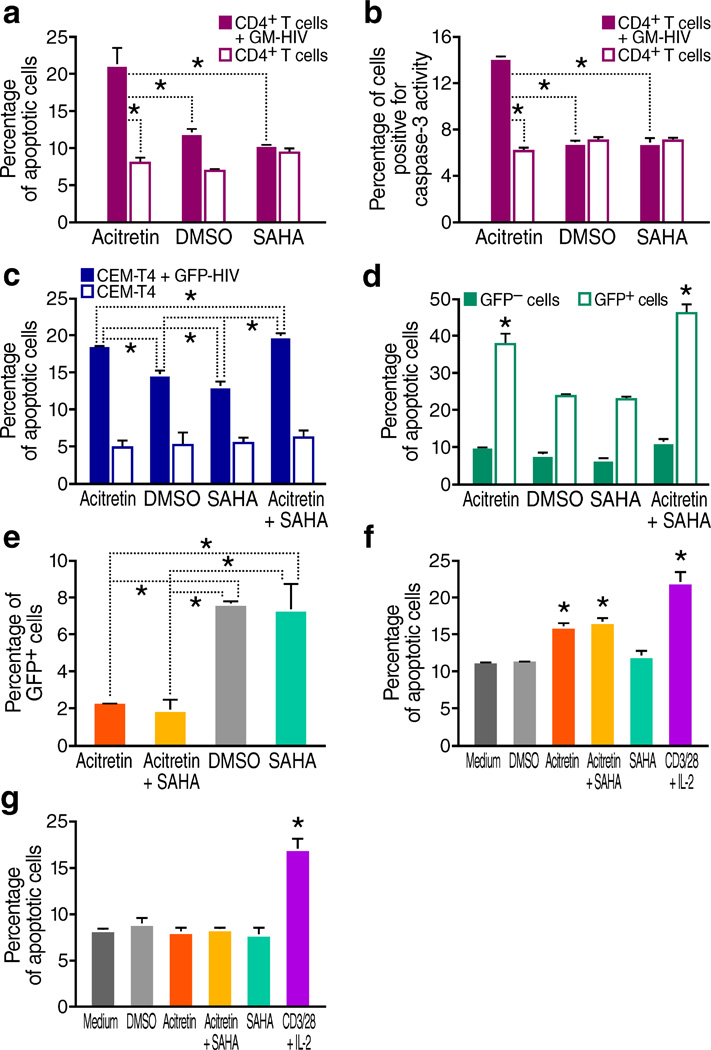
Figure 2.
Acitretin preferentially induces apoptosis in HIV-infected cells. (a) Percentage of apoptotic cells determined by annexin V staining of GM-HIV-infected or mock-infected CD4+Tcells after 72 h of treatment. The percentage of apoptotic cells was significantly greater in the presence of acitretin than with SAHA or DMSO in GM-HIV-infected but not uninfected CD4+T cells (P < 0.05). (b) Percentage of cells expressing active caspase-3 determined by flow cytometry assessed 72 h of treatment with DMSO, SAHA or acitretin. Caspase-3 activity was preferentially increased in GM-HIV infected CD4+T cells treated with acitretin (P<0.05). (c) Percentage of apoptotic cells determined by annexin V staining of GFP-HIV-infected and uninfected CEM-T4 cells. Acitretin and acitretin plus SAHA increased apoptosis at 48 h in GFP-HIV-infected cells to a significantly greater extent than SAHA or DMSO alone (P <0.05) although both of these agents produced higher than expected levels of cell death in infected cells compared to uninfected cells. No differences were detected in uninfected CEM-T4 cells. (d) Percentage of apoptotic cells determined by annexin V staining of infected cells from (c) gated for the presence or absence of expression of GFP encoded by the reporter virus. Acitretin and acitretin plus SAHA increased apoptosis of GFP-positive cells to a significantly greater degree than SAHA or DMSO, while no significant increases were induced by these agents in GFP negative cells (P < 0.05). (e) Percentage of GFP-positive cells after 7 d of treatment, as determined by flow cytometry of infected cells from (c). Both acitretin and acitretin plus SAHA reduced the number of GFP-HIV-positive cells significantly more (P < 0.05) than treatment with SAHA or DMSO. (f) Average percentage of apoptotic cells determined by annexin V staining of CD4+ T cells from HIV+ subjects on ART (n = 12). After 7 d of treatment with acitretin and acitretin plus SAHA, the frequency of apoptotic cells was significantly increased in patient CD4+ T cells compared to DMSO, SAHA, or medium (P < 0.05). Apoptosis was also significantly increased following treatment with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies beads plus IL-2 (CD3/28+IL-2) (P < 0.05). (g) Mean percentage of apoptotic cells determined by annexin V staining in cultures of CD4+ T cells from four healthy control subjects. Neither acitretin, nor acitretin plus SAHA induced higher levels of apoptosis than DMSO, SAHA, or medium at day 7 in these normal cells while increased apoptosis was observed when these normal cells were treated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies beads plus IL-2(CD3/28+IL-2) (P < 0.05). Values represent mean ± s.e.m. of duplicate samples from experiments with cells from 12 HIV+ subjects (f), values represent mean ± s.e.m. of triplicate samples for (a,b,c,d,e) from three independent experiments, and values represent mean ± s.e.m.of triplicate samples for (g) from four healthy donor CD4 T cells experiments. A student's t-Test was used to compare experimental conditions (a–g); **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.