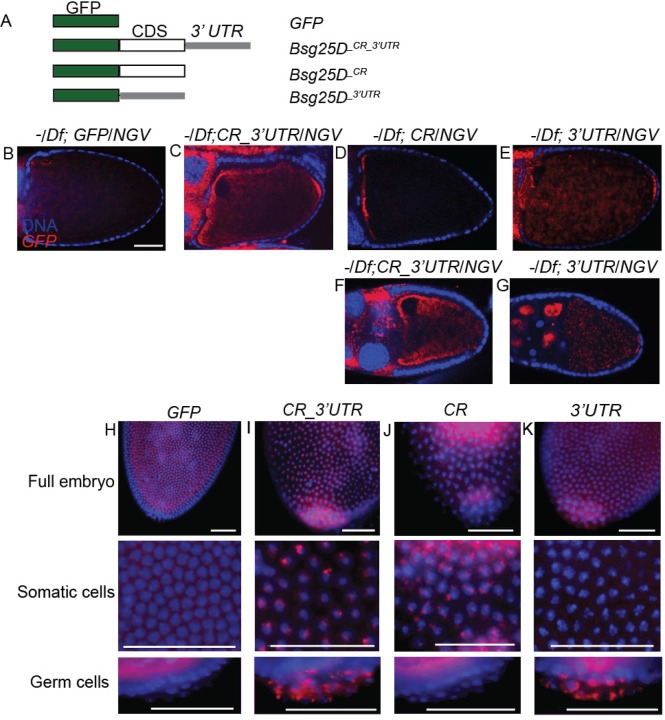
Fig. 3.
Bsg25D RNA contains localization elements within the coding region and 3′ UTR. (A) Schematic diagram of the transgenic constructs used, eGFP (green), Bsg25D-PB coding region (white), Bsg25D 3′ UTR (grey). (B-E) Distribution of transgenically-expressed mRNAs in stage 10 oocytes as shown by in situ hybridization, using a probe recognizing GFP, in the Bsg25D Null/Df(2L)6011 (−/Df) genetic background. The coding region alone promotes localization to the anterior pole, while the 3′ UTR promotes posterior localization. (F,G) Posterior localization is not apparent in early stage 10 oocytes expressing full-length GFP-Bsg25D (F) but is evident in similar stage oocytes expressing only GFP fused to the Bsg25D 3′ UTR (G). (H-K) Distribution of GFP-reporter mRNAs in early embryos expressing the transgenes as shown by in situ hybridization, using a probe recognizing GFP, in a wild-type genetic background. The 3′ UTR is essential for accumulation of these RNAs into the pole plasm and pole cells. All images scale bar=50 µm.