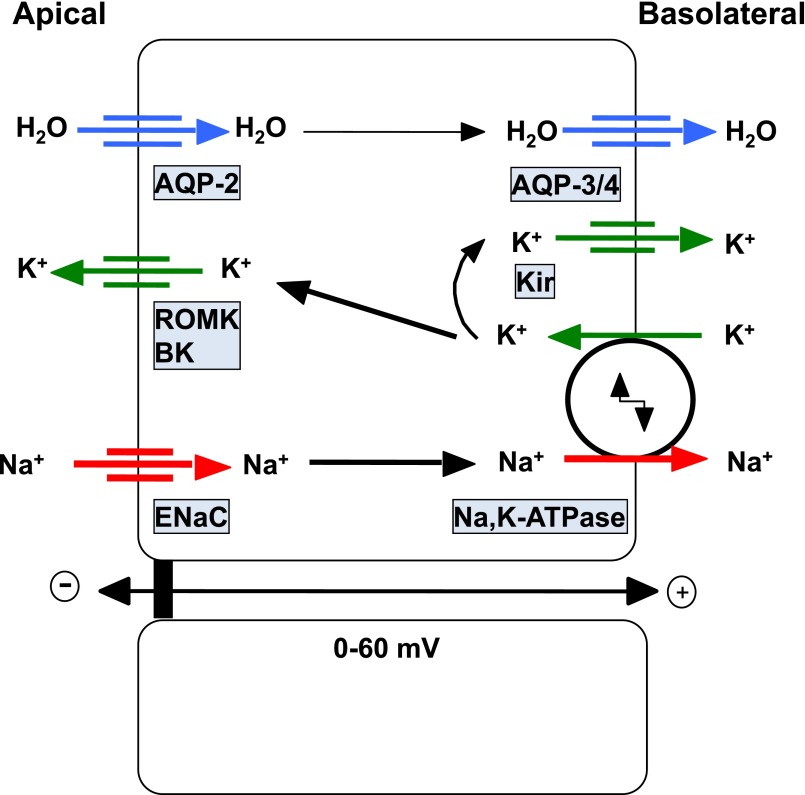
Figure 1.
Ion and water transporters in CD principal cells. Sodium reabsorption occurs sequentially through apical ENaC and basolateral Na+,K+-ATPase. This vectorial Na+ transport generates a lumen-negative transepithelial potential that drives potassium secretion via luminal K+-channels, i.e., ROMK and Big K+-channels (BK). The Na+,K+-ATPase generates the driving forces for both Na+ entry and K+ exit at the apical side of the cell. Basolateral K+ influx through Na+,K+-ATPase is also equilibrated by K+ efflux through basolateral K+-channels (Kir) to generate the negative resting transmembrane potential. Water permeability is mediated by sequential flow through apical AQP2 water channels and basolateral aquaporin-3 and -4 water channels.