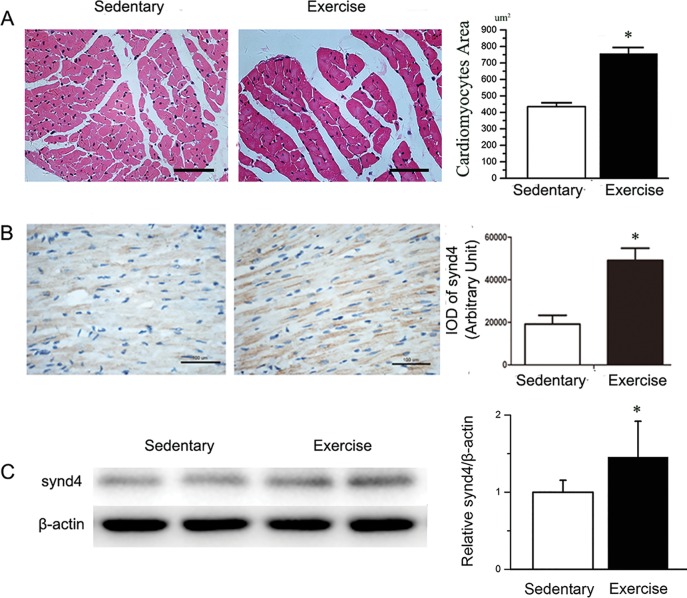
Figure 1.
Aerobic interval swimming training was used to induce physiological cardiac hypertrophy in rats, and synd4 was detected by immunohistochemistry assay and Western blot. (A) Histology analysis showed increases in cardiomyocyte surface area in Ex-rats compared with Sed-rats. *P < 0.05, Ex-rats versus Sed-rats; N = 6; scale bar = 100 μm. (B) Immunohistochemistry assay showed high intensity of synd4 expression in the cardiomyocytes of Ex-rats. *P < 0.05, Ex-rats versus Sed-rats; N = 6; scale bar = 100 μm. (C) Western blot showed increases of synd4 expression in myocardium after exercise. Data are shown as a ratio to β-actin and are expressed as a fold-increase when compared with Sed-rats. *P < 0.05, Ex-rats versus Sed-rats; N = 6; synd4: syndecan-4.