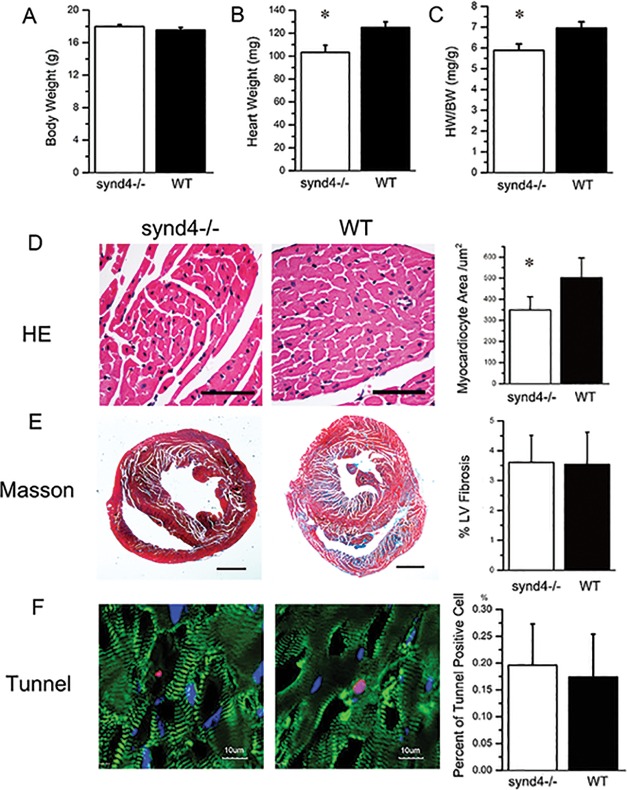
Figure 2.
Exercise-induced cardiac hypertrophy was blunted in the synd4–/– mice. (A to C): Histology analysis was used to detect body weight (BW), heart weight (HW) and HW/BW in synd4–/– and WT mice after exercise. (B) The HW and (C) HW/BW were increased in WT mice compared with synd4–/– mice after exercise. *P < 0.05, synd4–/– mice versus WT mice; N = 6. (D) Histology analysis showed enlargement of cardiomyocytes in WT mice after exercise. *P < 0.05, synd4–/– mice versus WT mice; N = 6; scale bar = 100 μm. (E) Masson stain showed no difference of Masson-positive fibrosis in synd4–/– and WT mice after exercise. *P < 0.05, synd4–/– mice versus WT mice; N = 6; scale bar = 1 mm. (F) Tunel analysis showed no difference of tunel-positive apoptosis cells in synd4–/– and WT mice after exercise. *P < 0.05, synd4–/– mice versus WT mice; N = 6; scale bar = 10 μm.