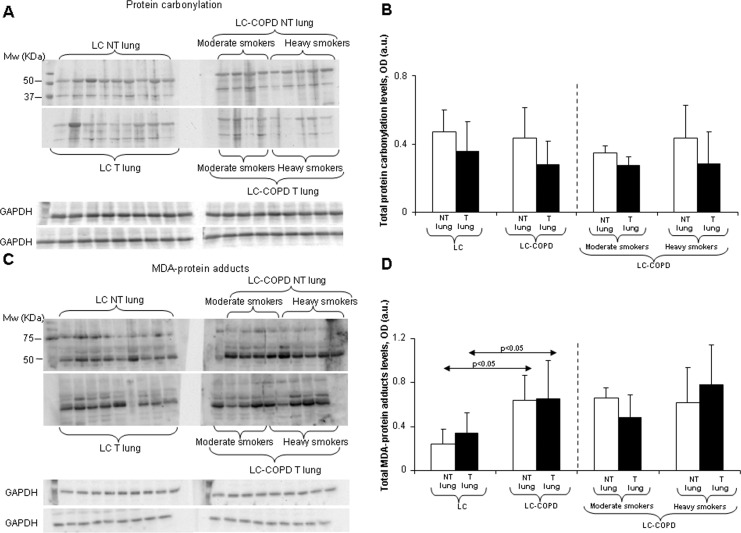
Figure 1.
(A) Immunoblots of total protein carbonylation in the lung tumor (T) and nontumor (NT) of LC and LC-COPD patients. (B) Mean values and standard deviation (optical densities [OD] expressed in arbitrary units [a.u.]) of total protein carbonylation levels in lung did not significantly differ between tumor (T) and nontumor (NT) lung samples and between any of the study groups of patients. The absence of any statistical sign means that no significant differences were found between groups for the different study comparisons. (C) Immunoblots of MDA–protein adducts in the lung tumor (T) and nontumor (NT) of LC and LC-COPD patients. (D) Mean values and standard deviation (OD expressed in a.u.) of total MDA–protein adduct levels in the lung were greater in LC-COPD as a group in both tumor (T) and nontumor (NT) lung samples compared with LC patients. The absence of any statistical sign means that no significant differences were found between groups for the different study comparisons. MW, molecular weights; KDa, kilodaltons.