Figure 4.
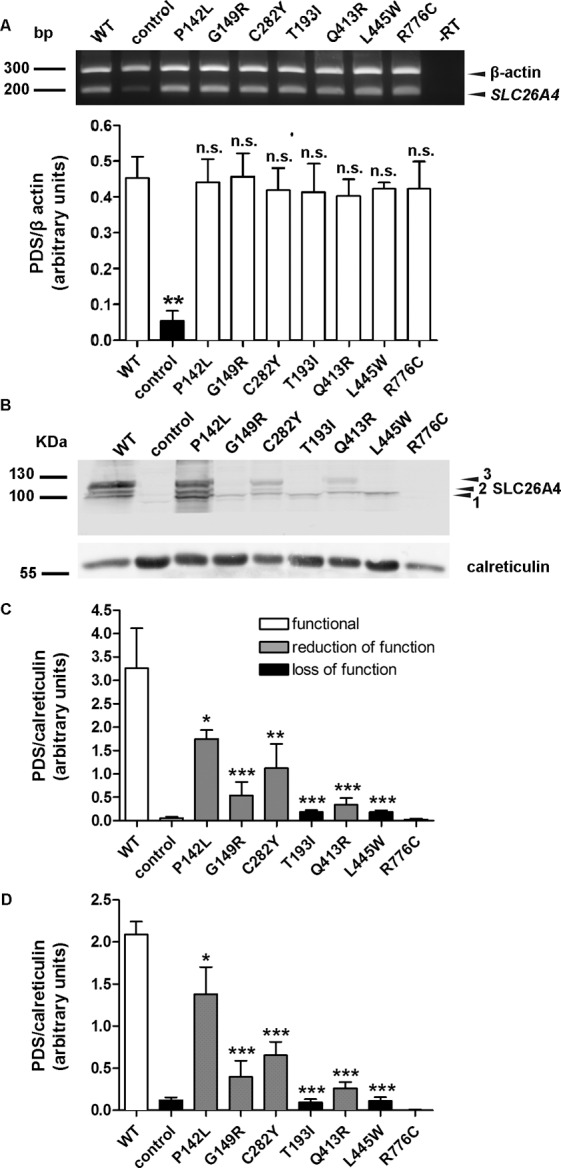
RNA and protein levels of wild-type pendrin and pendrin variants. (A) Top: The levels of the transcripts of wild-type pendrin and its variants, as well as the housekeeping gene β-actin, were detected by reverse transcription PCR in three independent samples of transfected HEK 293 Phoenix cells. In –RT, the PCR was conducted on a sample of total RNA that was not subjected to the reverse transcription reaction, to exclude genomic DNA contamination. For the control, cells were transfected with an empty vector. The presence of a weak band at 200 bp in control corresponds to endogenously expressed pendrin. Bottom: Densitometry of the pendrin signal normalized to the β-actin signal. n.s., Not significant, **p < 0.01 compared with wild-type, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparison posttest. (B) Representative immunoblotting on total cellular membrane extracts obtained after expression of untagged wild-type (WT) and mutated pendrin in HEK 293 Phoenix cells. For the control, cells were transfected with an empty vector. 1, 2 and 3 indicate the nonglycosylated, partially glycosylated and maturely glycosylated forms of pendrin, respectively. The expression levels of all (C) or only the maturely glycosylated (D) forms of wild-type (WT) and mutated pendrin were quantified by densitometry and normalized for the housekeeping protein calreticulin. n = 3, ***p < 0.005, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 compared with wild-type, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparison posttest.
