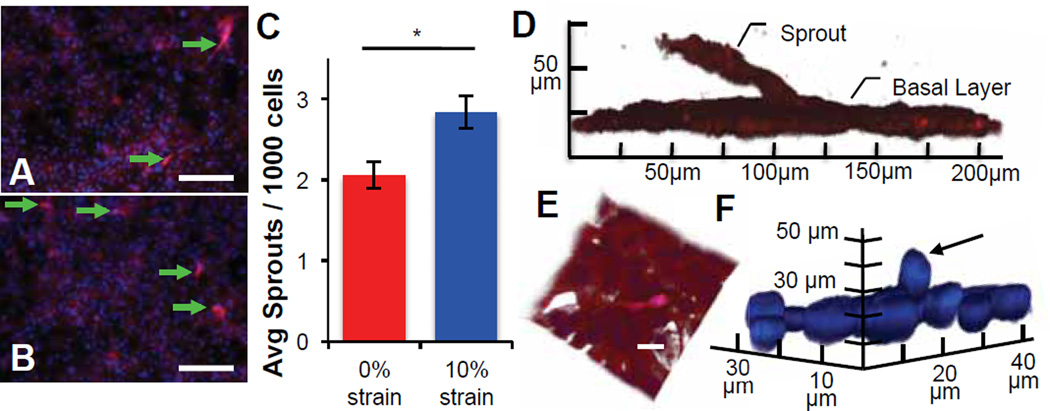
Fig. 3.
Static strain induces sprouting in capillary endothelial-derived monolayers. (A–B) Representative images of ECs demonstrate qualitatively increased sprouting into an overlying gel, after the application of (B) 10% uniaxial static strain as compared to (A) unstrained controls. (C) Quantification of sprouting images demonstrate a statistically significant increase in the average number of sprouts per 1000 DAPI-stained EC nuclei after 48 h of 10% static strain (* indicates significant difference, p = 0.005). Values reported as mean ± standard error of measurement. (D–F) Confocal renderings illustrating individual, out-of-plane sprout extension, visualized via (D) phalloidin-stained F-actin, (E) and composite with DAPI-stained nuclei show cellular process from sprouting tip cells extending into the gel; scale bar = 20 µm. (F) Out-of-plane nuclei can be seen extending from the monolayer (arrow) visualized with DAPI-stained nuclei and omission of actin for clarity.