Fig. 5.
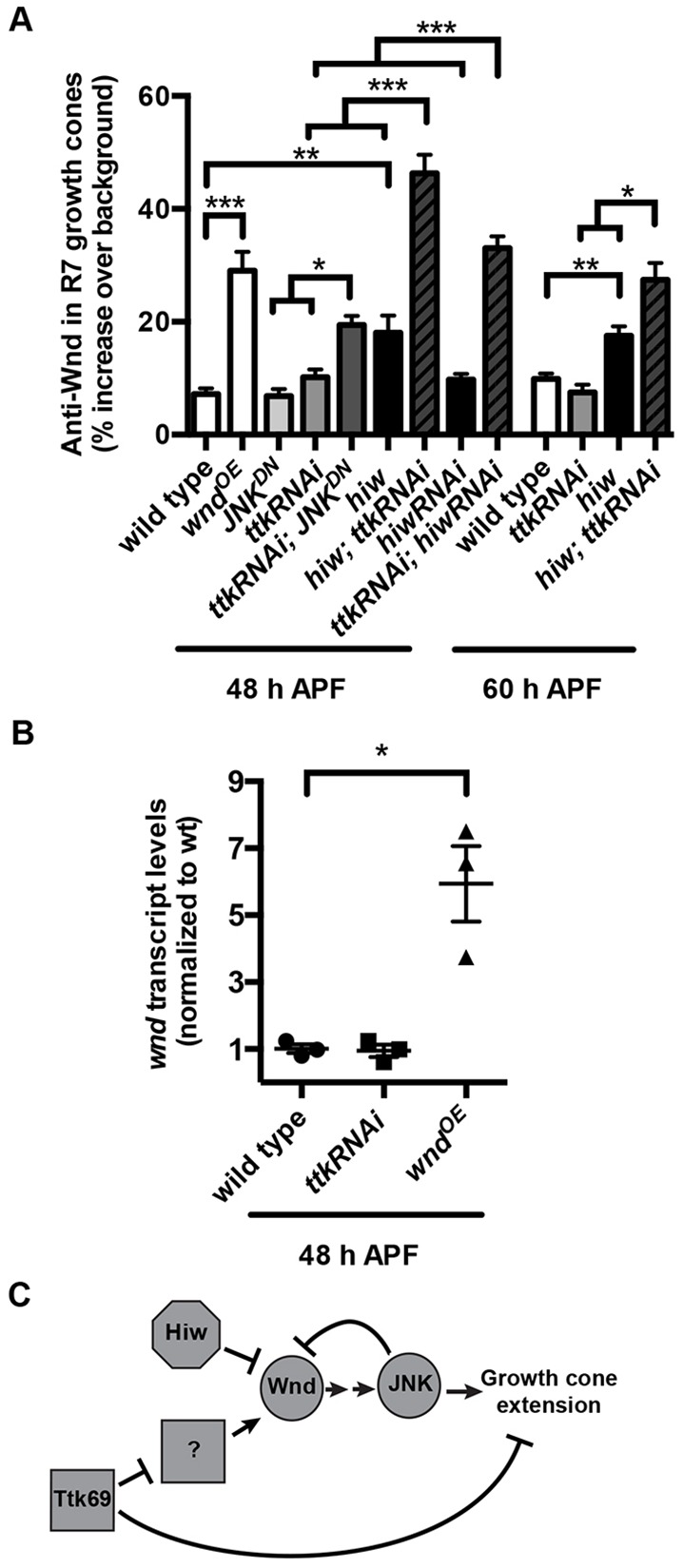
As R7 growth cones become presynaptic boutons, Ttk69 acts in parallel with Hiw and JNK-dependent negative feedback to repress Wnd. (A) Quantification of anti-Wnd levels in R7 axon terminals at 48 and 60 h APF (29°C). Loss of hiw alone moderately increases Wnd levels in R7 axon terminals at both time points (note: values for wild type and hiw mutant at 60 h APF are reproduced from Fig. 1). This increase is significantly less than that caused by chp-Gal4-driven expression of UAS-wnd (wndOE). Loss of ttk69 alone from R neurons (caused by ttk RNAi) has no significant effect on Wnd levels in R7 axon terminals. However, loss of both hiw and ttk69 causes a striking, significantly greater-than-additive increase in Wnd levels in R7 terminals at both time points. This increase was observed not only when R neurons expressed ttk RNAi in hiw null mutant animals but also when R neurons co-expressed ttk RNAi and hiw RNAi. Similarly, loss of JNK alone (caused by JNKDN) has no significant effect on Wnd levels, but loss of both JNK and ttk69 (caused by co-expression of ttk RNAi and JNKDN) results in a significantly greater-than-additive increase in Wnd levels in R7 axon terminals. *P<0.01, **P<0.001 and ***P<0.0001 based either on two-tailed t-tests for pairwise comparisons or a two-way ANOVA to test for greater-than-additive effects of disrupting two genes (Slinker, 1998). Error bars represent s.e.m. n=19, 12, 11, 12, 19, 15, 11, 21, 16, 16, 17, 8 and 11 brains from left to right on the graph. (B) Quantification of retinal wnd transcript levels at 48 h APF measured by qRT-PCR. Retinas in which all R neurons express ttk RNAi under the control of chp-Gal4 have wnd transcript levels that are not significantly different from those in wild type; retinas in which R neurons express wnd under the control of chp-Gal4 do have significantly increased wnd transcript levels (*P<0.01). n=3 biological replicates, error bars represent s.e.m. (C) Model summarizing the roles of Hiw, Wnd, JNK and Ttk69 in R7s as their growth cones become presynaptic boutons.
