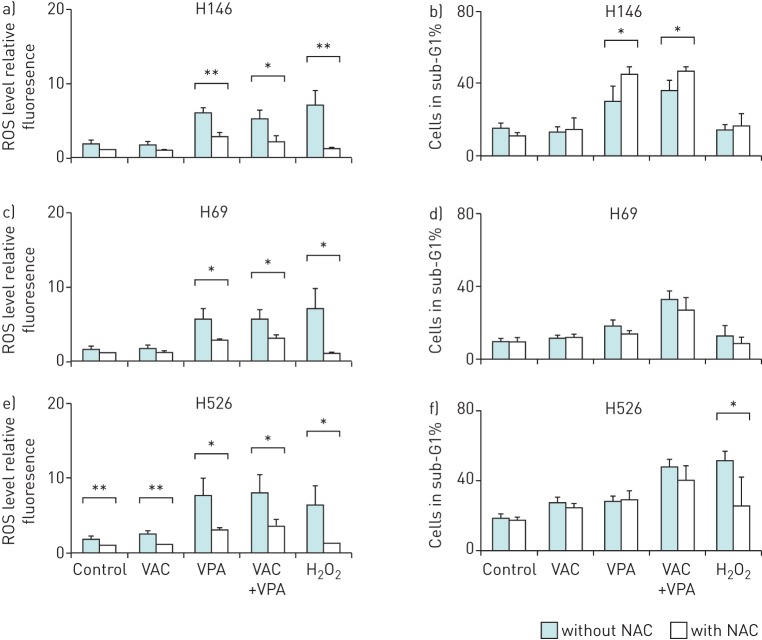
FIGURE 3.
Valproic acid (VPA)-induced apoptosis is independent of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Three small cell lung cancer cell lines (H146 (a and b), H526 (c and d) and H69 (e and f)) were incubated 1 h with or without 10 mM N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a ROS scavenger. Then, the cells were cultivated for 24 h with or without VPA (1 mM) in combination with mafosfamide (10 µM), vindesine (20 nM) and doxorubicin (0.3 µM). Prior to the addition of the drugs, cell cultures were split into two fractions. The first was incubated for 1 h in presence of 5 µM 5,6-chloromethyl-2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate acetyl ester at 37°C in order to detect the ROS levels by flow cytometry. 500 µM hydrogen peroxide was used as positive control for ROS production. a, c and e) Data are presented as mean±sd fluorescence intensity of chloromethyldichlorofluorescein related to the level obtained in control. b, d and f) The remaining cell fraction was used to determine the rates of apoptosis by flow cytometry after ethanol fixation and propidium iodide staining. Data are represented as mean±sd of three independent experiments. For clarity, statistical tests between conditions and their associated control are indicated above individual conditions. *: p<0.05 by paired Student's t-test; **: p<0.01 by paired Student's t-test.