FIGURE 2.
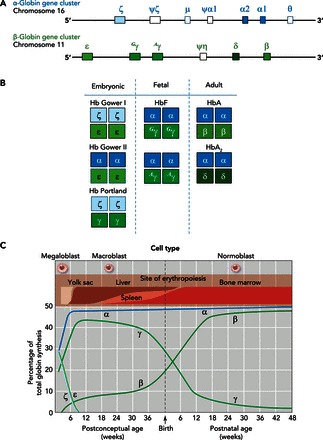
The expression of α- and β-type globin genes is developmentally regulated, resulting in the synthesis of functionally distinct isoHbs
A: structure of the human α- and β-globin gene clusters. B: the set of structurally distinct embryonic, fetal, and adult Hb isoHbs, with subunits encoded by each of the pre- and postnatally expressed α- and β-type genes. C: developmental timeline for changes in the expression levels of the various α- and β-type genes from the earliest stages of embryogenesis to the end of the first year of life. C was adapted from Ref. 106 with permission from British Medical Bulletin.
