Figure 1.
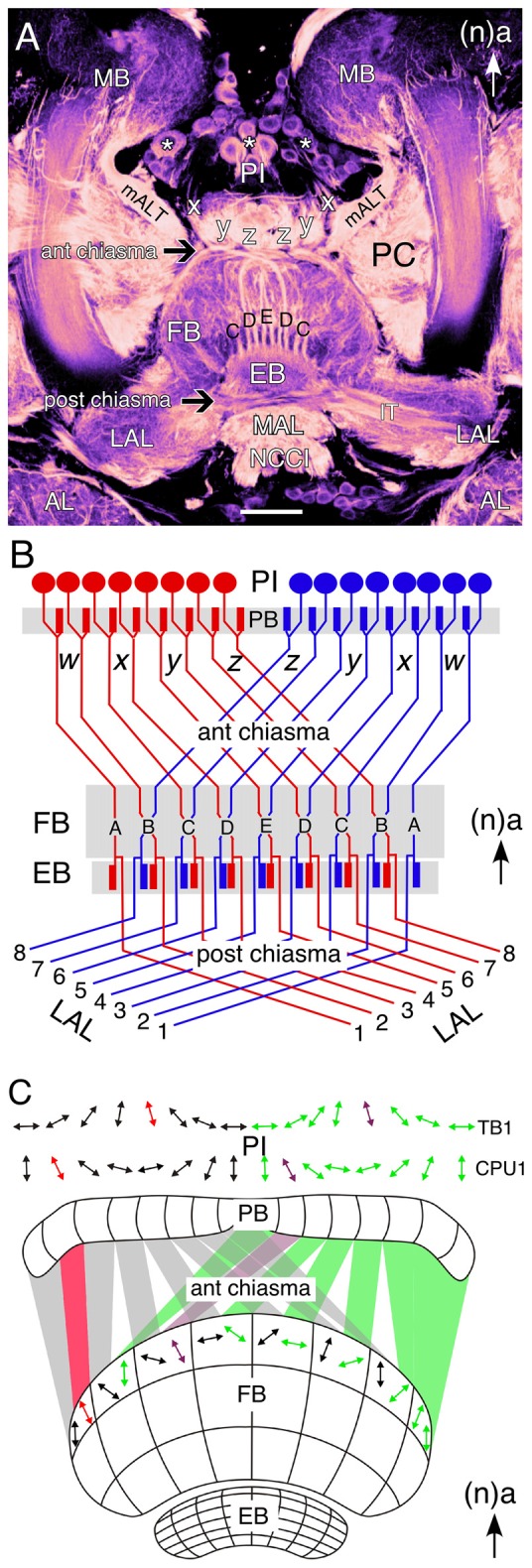
Wiring of the central complex subserves information processing. (A) Confocal image of a brain slice in an adult grasshopper (Schistocerca gregaria) following 8 B7 immunolabeling reveals the neuroarchitecture of the central complex between the bilateral mushroom bodies (MB) in the central brain. Neurons (white stars) of the pars intercerebralis (PI) direct axons via the w, x, y, z tracts into a chiasmal system (black arrow) anterior to the fan-shaped body (FB). These fibers then form columnar bundles (of which C, D, E, D, C are visible) in the FB and project further to the ellipsoid body (EB) and via a posterior chiasmal system (black arrow) laterally in the isthmus tract (IT) to the lateral accessory lobes (LAL). Note that the FB is also termed the upper division of the central body, and the EB the lower division of the central body (see Müller et al., 1997; Heinze and Homberg, 2008). White arrow points to anterior (a) according to the neuraxis (n) and is repeated for emphasis in all panels. (B) Wiring diagram (not to scale) illustrates the essential plan of axon projections from neurons of the PI via the protocerebral bridge (PB) into the w, x, y, z tract system of the left (red) and right (blue) protocerebral hemsipheres and hence via the anterior chiasmal system to form nine columns (A–E) in the FB and EB of the central brain. Axons subsequently exit the EB posteriorly and project via a posterior chiasmal system to the bilateral LALs. (C) Schematic (not to scale) illustrates the preferred polarization sensitivities (double arrows) of tangential (TB1) and columnar (CPU1) neurons in the PI of the grasshopper and the way these sensitivities are projected via the anterior chiasmal system to be represented within the columnar neuroarchitecture of the FB (CBU; see panel B). Other abbreviations: mALT, medial antennal lobe tract; AL, antennal lobe; MAL, median accessory lobe; NCCI, nervus corporis cardiaci I; PC, protocerebrum. Scale bar in (A) represents 100 μm. Panel (A) modified from Boyan et al. (2015) with permission; panel (B) modified from Williams (1975) with permission; panel (C) personal communication courtesy of U. Homberg.
