Figure 10.
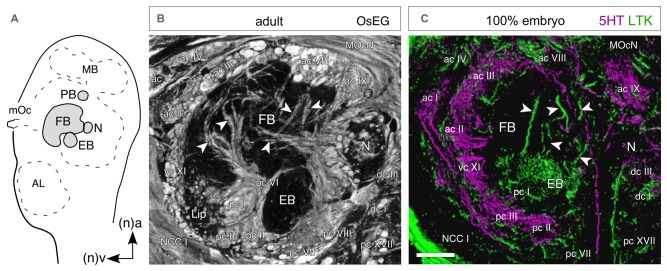
Temporal topology of neurochemical expression reflects architecture of the central complex. (A) Schematic (not to scale) shows the location of central complex modules in the brain as seen in sagittal view. Abbreviations: MB, mushroom body; mOc, median ocellus; FB, fan-shaped body; N, nodulus; EB, ellipsoid body; AL, antennal lobe. Arrows point to anterior (a) and ventral (v) according to the neuraxis (n). Axes apply to all panels. (B) Histological (sagittal) section of the central complex in the adult brain following osmium ethyl gallate staining reveals axon profiles in anterior (ac), posterior (pc), ventral (vc) and dorsal (dc) commissures circumscribing the FB, EB, N and ventral lip. Other fiber tracts seen are the median ocellar nerve (MocN) and nervus corporis cardiaci I (NCC I). (C) Confocal image of a parasagittal section through the central complex at 100% of embryogenesis following 5HT (magenta) and LTK (green) double labeling. There is no co-expression (absence of white) in the commissural and columnar (white arrowheads) neuroarchitecture of the central complex. Since 5HT and LTK are expressed by neurons of different ages (see Figure 7), the co-labeling provides a temporal insight into the neuroarchitecture of the central complex. Scale bar in (C) represents 40 μm in (B), 100 μm in (C). Modified from Boyan et al. (2010a).