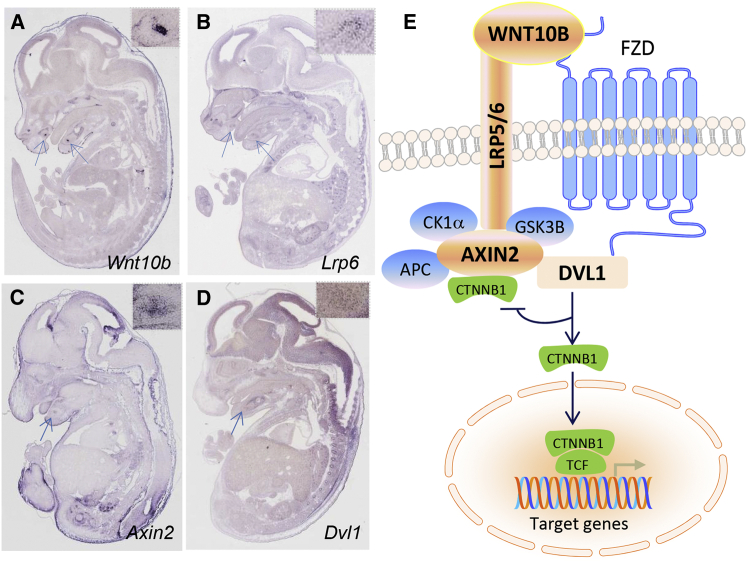
Figure 3.
Expression of Wnt10b in Embryonic Mice and the Wnt Pathway
(A) Wnt10b expression was detected in the developing tooth region by in situ hybridization, as indicated by arrows in the sagittal section of an E14.5 embryo (Eurexpress). The region of interest is shown in the inset.
(B) Lrp6 expression is shown as in (A).
(C) Analysis of Axin2 expression is shown as in (A).
(D) Expression of Dvl1 is shown as in (A). All expression data in Eurexpress are publically available; users can retrieve information tailored to their own needs.
(E) The binding of WNT10B ligand to a dual-receptor complex comprising the Wnt co-receptors LRP5 and LRP6 and one of the seven transmembrane receptors of the FZD family (e.g., Frizzled-8 [encoded by FZD8 (MIM: 606146)]) initiates Wnt-β-catenin signaling. AXIN2 moves to the LRP5-LRP6 tail at the membrane through its interaction with dishevelled (DVL1), which is recruited by FZD. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β (encoded by GSK3B [MIM: 605004]) is also included in this complex, which prevents phosphorylation of β-catenin (encoded by CTNNB1 [MIM: 116806]) and its proteosomal degradation. β-catenin is therefore accumulated in the cytoplasm and translocated into the nucleus, where it associates with members of the TCF and LEF transcription factor families to control transcription of target genes. In addition to WNT10A variants, variants in several Wnt-pathway components, including WNT10B, LRP6, AXIN2, and DVL1 (nodes in orange), have been found to cause tooth agenesis.