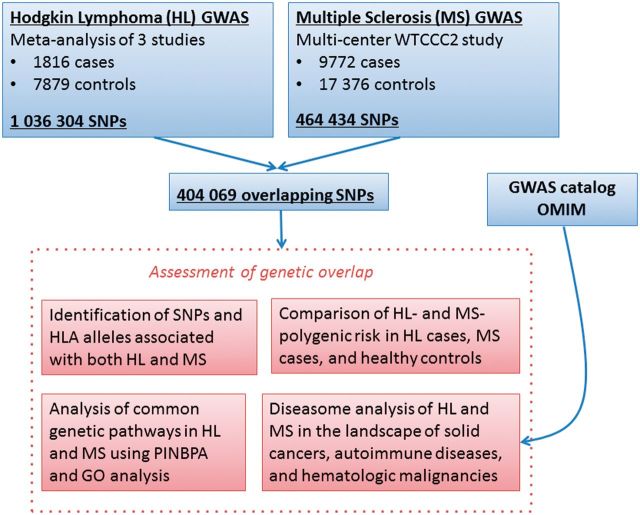
Figure 1.
Study design and data analysis procedures. Results from previously reported genome-wide associations studies (GWAS) of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and multiple sclerosis (MS) were used to assess genetic overlap between the two diseases. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) independently associated with both HL and MS were identified, and disease-specific polygenic risk scores were compared in HL cases, MS cases and healthy controls. Protein-interaction network-based pathway analysis (PINBPA) was performed on the intersection of nominally associated ( P < 0.05) SNPs in HL and MS and gene ontology (GO) analysis was performed to identify common genetic pathways. Genetic similarity between HL and MS was further evaluated in the context of other immune diseases, haematological malignancies and solid cancers by constructing a diseasome using data from previously reported GWAS.