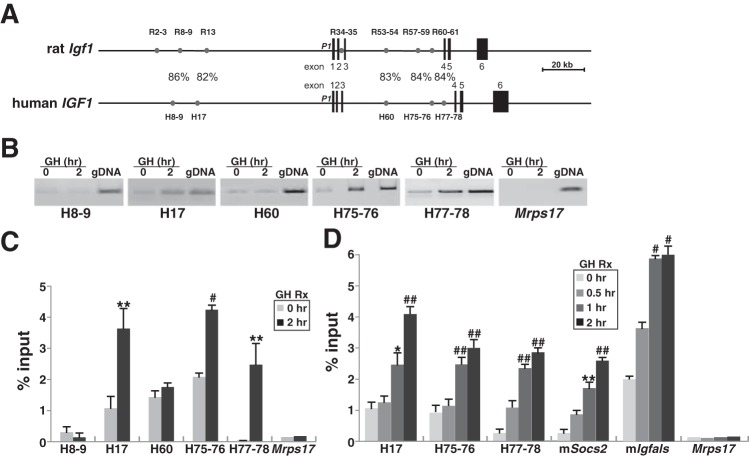
Fig. 4.
GH induces recruitment of STAT5b to potential binding elements in chromatin within the human IGF-I locus. A: comparison of rat Igf1 and human IGF1 loci. Depicted in addition to the genes are 7 previously identified GH-regulated STAT5b-binding elements in the rat Igf1 locus and 5 analogous regions in the human IGF1 locus (gray circles) and a scale bar. %Identity for each element between species is shown. B–D: results of chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments using chromatin harvested from C310T1/2 human IGF1 BAC clone 3 after addition to cells of recombinant rat GH (40 nM) for 0, 0.5, 1, or 2 h are depicted. Primer pairs are listed in Table 4. B: results from 1 experiment of binding of STAT5b to DNA in chromatin at the 5 conserved putative STAT5-binding elements depicted in A plus a control primer pair from mouse Mrps17 in cells prior to and 2 h after GH addition. C: results of binding of STAT5b to DNA in chromatin at the 5 conserved putative STAT5-binding elements seen in A plus a control primer pair from mouse Mrps17 in cells before and 2 h after GH addition (means ± SD of 4 independent experiments: **P < 0.02 and #P < 0.01 vs. time 0). D: time course of binding after GH treatment of STAT5b to DNA in chromatin at the 5 conserved putative STAT5-binding elements shown in A plus the control primer pair from mouse Mrps17 (means ± SD of 4 independent experiments: **P < 0.02, #P < 0.01, and ##P < 0.005 vs. time 0).