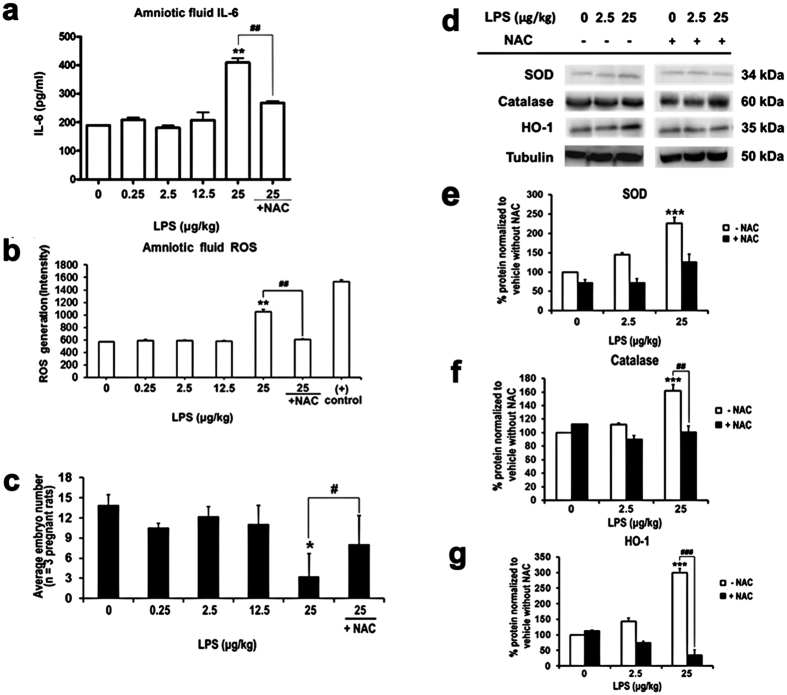
Figure 2. NAC prevented LPS caused ROS response and intra-uterine fetal death.
(a) The IL-6 levels in amniotic fluid was detected by ELISA. The results show that intra-uterine LPS application caused significantly increased of amniotic IL-6 at highest does (25 μg/kg), and addition of NAC reduces this upregulation. n = 3 assays, each performed in duplicate. (b) Cm-H2DCFDA detection kit was used to determine the LPS-induced ROS generation in amniotic fluid. The highest concentration of LPS (25 μg/kg) dramatically induced ROS generation in amniotic fluid, and addition of NAC decreased this outcome. n = 3 assays, each performed in duplicate. (c) The number of embryo was decreased in response to LPS exposure. n values (number of pregnant female rats) for 0 μg/kg LPS = 11; 0.25 μg/kg LPS = 3; 2.5 μg/kg LPS = 5; 12.5 μg/kg LPS = 5; 25 μg/kg LPS = 5; 25 μg/kg LPS plus NAC = 5. (d) Representative Western blot of antioxidative markers in extract from five independent experiments is shown. (e) Quantitative analysis of SOD/tubulin band intensity shows an increase expression of SOD in a dose dependent manner, and the application of NAC eases the effect. n = 5. (f) Quantitative analysis of catalase /tubulin band intensity shows that high dose of LPS significantly induces catalase expression, and NAC hinders the act of LPS. n = 5. (g) Quantitative analysis of HO-1/tubulin band intensity shows an up-regulation of HO-1 in response to LPS, and addition of NAC dose-dependent reduces the HO-1 expression. *Statistically different from vehicle condition without NAC. #Statistically different from each LPS dosage compared to NAC. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer Multiple Comparisons Test. n = 5.