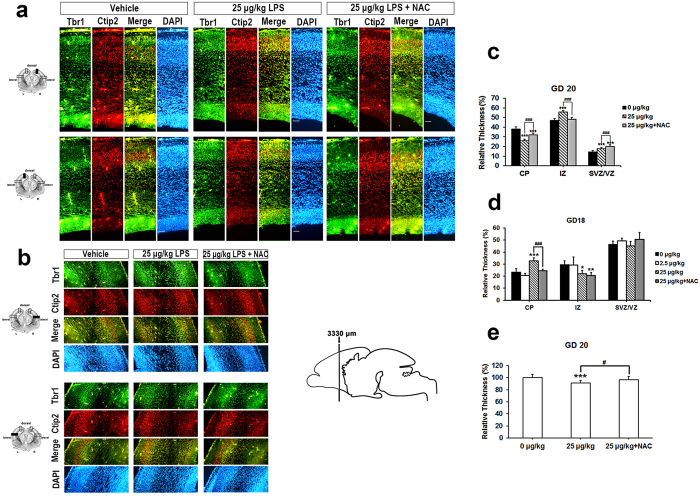
Figure 7. NAC restored the sustainable effects of LPS on the late embryonic brain development.
Coronal sections of indicated GD 20 rat embryonic brains were immunostained for Tbr1, Ctip2 and DAPI. Five embryo brains were randomly selected from at least three different pregnant rats. In each brain, two coronal section near the site around 2380 μm from the front of olfactory bulb were analyzed. Representative images of the sections at cortical dorsal (a) and lateral (b) areas from three independent experiments are shown. Tbr1+ cells are distinguished from Ctip2+ cells in vehicle condition, but interlaced at LPS treated group. Scale bar, 50 μm. (c) The portion of dorsal cortical plate (CP), intermediate zone (IZ), and sub-ventricular and ventricular zone (SVZ/VZ) relative to total thickness from the edge of ventricle to the top surface of the GD 20 brain were determined. LPS causes a significant decrease in CP thickness compared to vehicle condition. ***p < 0.001 by Unpaired t test in each zone. (d) The portion of dorsal cortical plate (CP), intermediate zone (IZ), and sub-ventricular and ventricular zone (SVZ/VZ) relative to total thickness from the edge of ventricle to the top surface of the GD 18 brain were determined. CP portion was dramatically increased in LPS treated group, which was returned to vehicle condition in the presence of NAC. *** or ###p < 0.001 by ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer Multiple Comparisons Test or Dunn’s Multiple Comparisons Test. (e) Quantifications of the differences in the thickness of the dorsal cortex. Histograms represent the means ± SD. n = 10. ***p < 0.001 by Student’s-t Test.