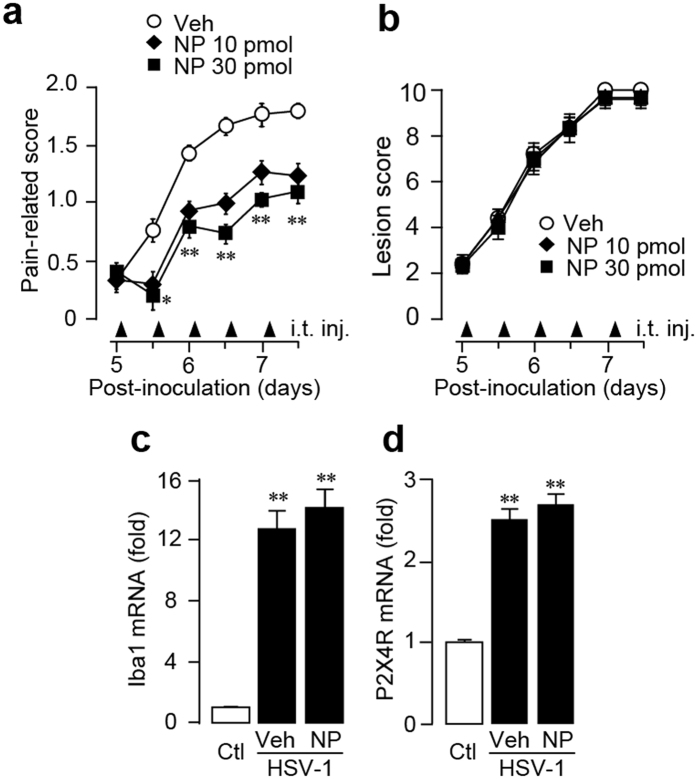
Figure 5. Anti-allodynic effect of NP-1815-PX in herpetic pain model.
(a,b) Effect of intrathecally administered NP-1815-PX on induction of HSV-1-evoked mechanical allodynia (a) and skin lesions (b) on day 5 to 7 after HSV-1 inoculation in mice. Mechanical allodynia was assessed with a pain-related score following light brushing of the hindpaw. Skin lesions were assessed with a lesion score. The pain-related scores and skin lesion scores were examined at day 5 to 7. NP-1815-PX or vehicle (Veh: PBS) was intrathecally administered (i.t. inj.) twice daily from day 5 to 7 (closed triangles indicated on horizontal X-axis). Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 5–6, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. vehicle control group). (c,d) Real-time PCR analysis of Iba1 and P2X4R mRNA expression in total RNA extracted from the spinal dorsal horn (day 6) in normal mice (Ctl) and in HSV-1-inoculated mice intrathecally treated with vehicle (Veh: PBS) or NP-1815-PX. Values represent the relative ratio of Iba1 and P2X4R mRNA expression (normalized to GAPDH mRNA value) to normal mice (Ctl). Data represent mean ± SEM [n = 3–4, **P < 0.01 vs. normal mice (Ctl)].