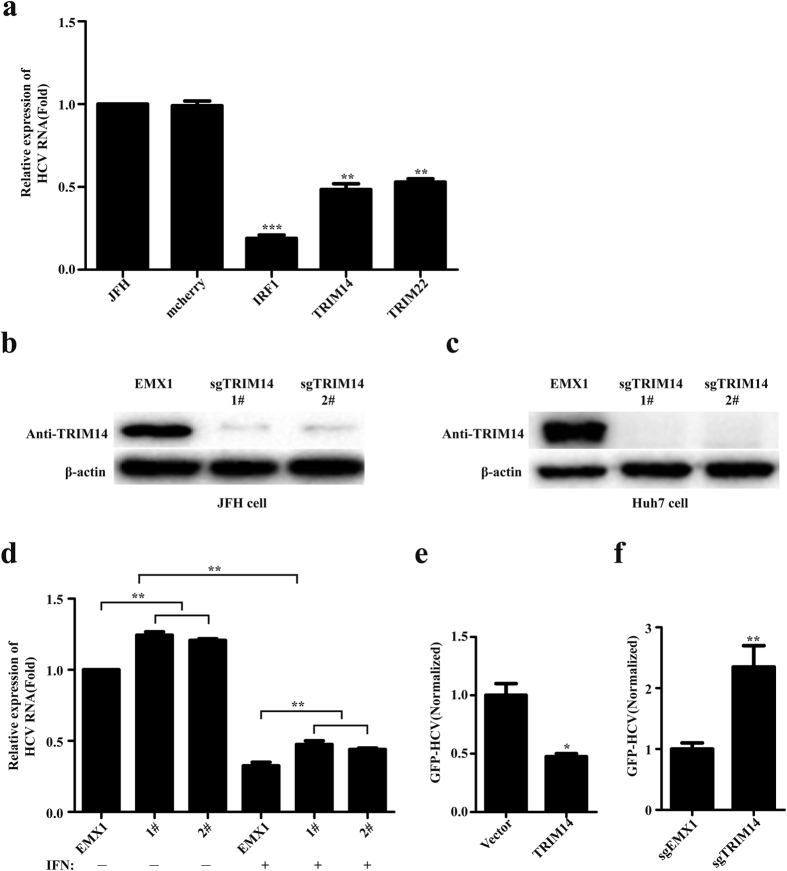
Figure 1. TRIM14 suppresses HCV infection and replication.
(a) Effect of TRIM14 on HCV replication. TRIM14 was over expressed in JFH cells, quantitative real-time PCR method was used to detect the replication of HCV, mcherry served as a negative control, while IRF1 and TRIM22 as positive controls. (b) Immunoblot analysis of protein expression of TRIM14 in JFH knockout cells constructed by using CRISPR/Cas9. JFH monoclonal cells (1# or 2#) were harvested and analyzed by western blot to determine the knockout efficiency of TRIM14 in JFH cells. (c) Knockout of endogenous TRIM14 by CRISPR/Cas9 detected by western blot in Huh7 cells. (d) Effect of knockout of TRIM14 on HCV replication. Knockout of TRIM14 monoclonal cells (1# or 2#) were treated with or without IFN for 24 hours and analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR to determine the relative expression of HCV replicon. (e) Effect of TRIM14 on HCV-GFP infection. HCV-GFP was quantified by the calculated value of the percentage% GFP-positive population andMFI of GFP signal. (f) Effect of knockout of TRIM14 on HCV-GFP infection. HCV-GFP was quantified by the calculated value of the percentage% GFP-positive population and MFI of GFP signal. All experiments were performed in triplicates and data shown are representative of three independent experiments with SEM indicated by error bars. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.