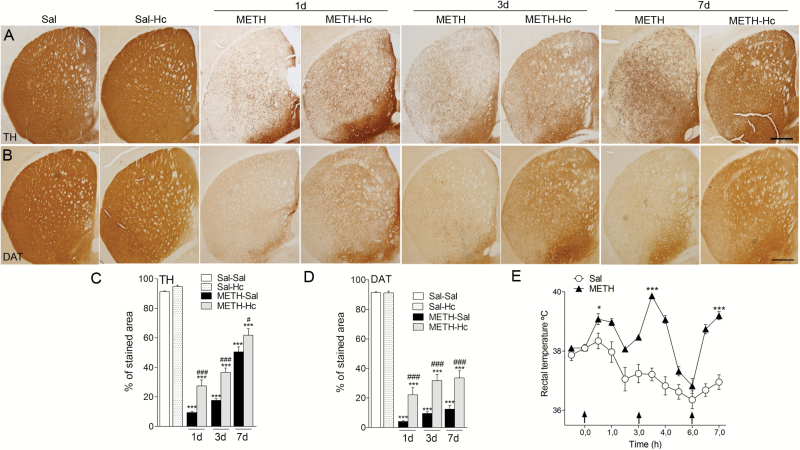
Figure 1.
C-terminal domain of the heavy chain of tetanus toxin (Hc-TeTx) attenuated methamphetamine (METH)-induced decreases in tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and dopamine transporter (DAT) expression in the striatum. Hc-TeTx (Hc) prevents the striatal TH and DAT decrease induced by METH. Photomicrographs of striatal sections stained for TH (A) and DAT (B) from mice at 1, 3, and 7 days after METH with and without Hc-TeTx treatment. Histograms show the percentage of striatal stained area of TH-immunoractive (TH-ir) (C) and DAT-ir (D) in the striatum. (E) METH (4mg/kg, 3 consecutive administrations each 3 hours apart) produced hyperthermia in mice after the injections Arrows indicate drug injections. Data represent mean±SEM, n=6–8/group, using 4–5 sections/animal. *P<.05, ***P<.001 vs saline group, #P<.05, ###P<.001 vs METH only. Bar indicates 500 µm.