Figure 4.
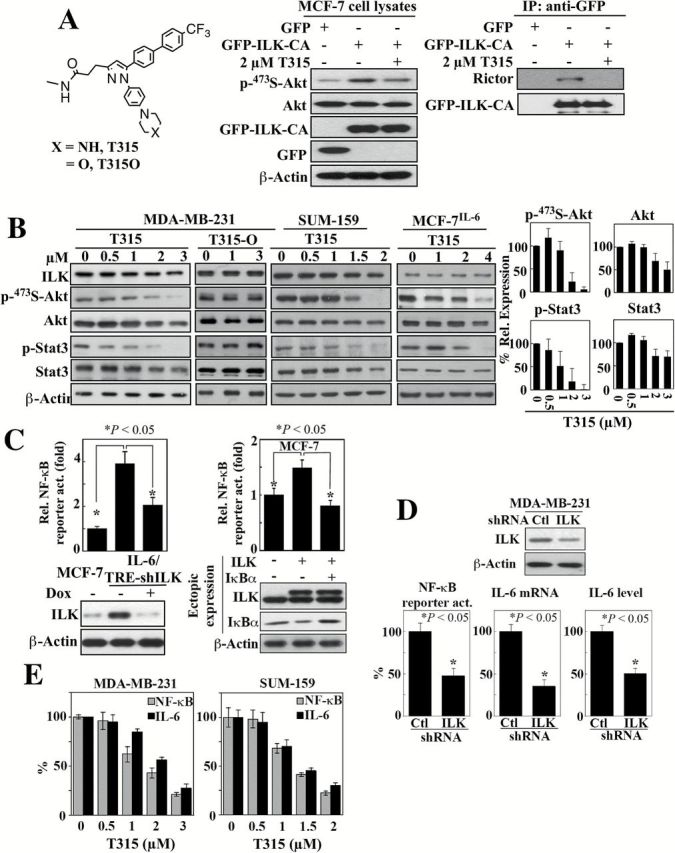
Evidence that ILK acts as a molecular switch for the IL-6-NF-κB feedback loop. (A) Left, structures of the ILK inhibitor T315 and its inactive analogue T315O. Middle and right, The effect of ILK inhibitor T315 (2 μM, 48-h treatment) on Akt phosphorylation (middle) and the interaction between ILK and Rictor (right) in MCF-7 cells ectopically expressiing GFP-tagged constitutively active (CA) ILK. IP, immunoprecipitation. (B) Western blot analysis of the dose-dependent effects of T315 and/or T315O (48-h treatment) on the expression/activation status of ILK and IL-6 downstream signaling markers, Akt and Stat3 in MDA-MB-231, SUM-159 and MCF-7IL-6 cells. Left, Representative blots. Right, Corresponding densitometric analysis of western blots showing relative abundance of p-473S-Akt and p-Stat3 after normalization to corresponding total protein, and Akt and Stat3 after normalization to β-actin in MDA-MB-231 cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). (C) Left, suppressive effect of shRNA-mediated knockdown of ILK on NF-κB luciferase reporter activity in MCF-7IL-6 cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Right, effect of ectopic expression of ILK on NF-kB luciferase reporter activity in MCF-7 cells and its reversal by the enforced expression of the IκBα super-repressor. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Changes in ILK and IκBα protein expression levels were confirmed by western blot (lower panels). (D) Suppressive effect of shRNA-mediated knockdown of ILK on NF-κB reporter activity, IL-6 mRNA expression, and secreted IL-6 abundance in culture medium in MDA-MB-231 cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Change in ILK protein expression was confirmed by western blot (upper panel). (E) Dose-dependent suppressive effects of T315 (24-h treatment) on NF-κB reporter activity and IL-6 mRNA expression (by qPCR) in MDA-MB-231 and SUM-159 cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
