Fig. 5.
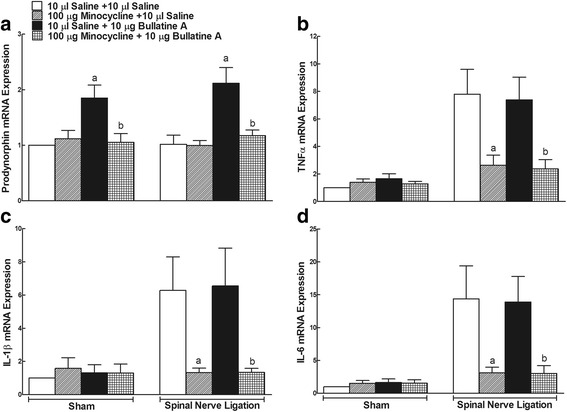
Effects of the intrathecal injection of bullatine A on the gene expression of prodynorphin (a) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (b), interleukin (IL)-1β (c), and IL-6 (d) in sham rats and neuropathic rats. Peripheral neuropathy was induced by the tight ligation of L5/L6 spinal nerves, and sham rats were under the same procedure except for the spinal nerves which were not ligated. The ipsilateral spinal lumbar enlargements were obtained 1 h after the intrathecal injection of saline or bullatine A (10 μg). The expression of prodynorphin and pro-inflammatory cytokines was measured by real-time quantitative PCR relative to the gapdh gene. The data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 6 in each group). Symbols a and b denote statistical difference compared with the saline plus saline group and saline plus bullatine A group in sham or neuropathic rats (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by the post hoc Student–Newman–Keuls test)
