Fig. 1.
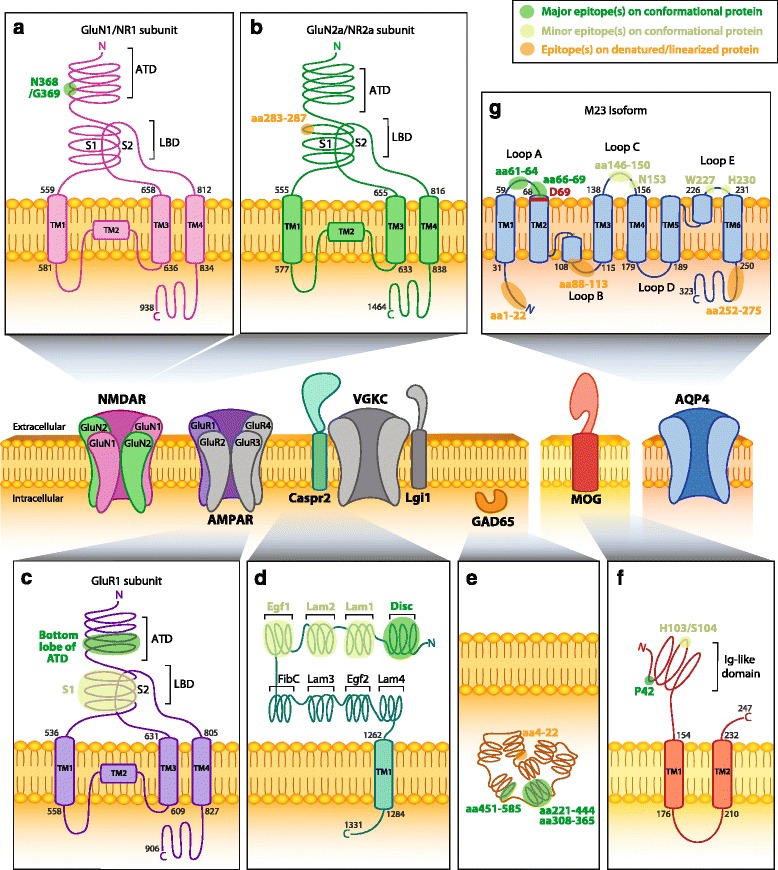
Epitopes of human CNS autoantibodies. Two subtypes of ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) are the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) and the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR). Subunits of NMDAR (a, b) and AMPAR (c) contain an extracellular amino terminal domain (ATD) and a ligand-binding domain (LBD) formed by segment 1 (S1) and segment 2 (S2). Anti-NMDAR antibodies recognize amino acid (aa) N368 and G369 which reside on the bottom lobe in the ATD of the GluN1 subunit (a, Q05586) [35]. Anti-NMDAR antibodies also bind to an epitope at aa283-287 within S1 of the LBD in subunits GluN2a and GluN2b (b, Q12879; only GluN2A is shown) [67]. Anti-AMPAR antibodies are directed against an extracellular epitope within the bottom lobe in the ATD of the GluR1 subunit (c, P42261), but specific aa in the ATD have not been mapped [32]. d Contactin-associated protein 2 (Caspr2, Q9UHC6) consists of eight domains and forms part of the voltage-gated potassium channel (VGKC) complex with the leucine-rich glioma-inactivated protein 1 (Lgi1). Anti-Caspr2 antibodies recognize the extracellular N-terminal half (domains I–IV; discoidin (Disc), lamininG (Lam)-1, Lam2, and epidermal growth factor 1 (Egf1), respectively), but most commonly bind to an epitope within the Disc domain [37, 38]. e Anti-cytoplasmic enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 (GAD65) antibodies recognize an epitope at aa221-444 [48], aa451-585, and aa308-365 [47]. Anti-GAD65 antibodies have also been shown to bind to linearized protein at aa4-22 [47]. f Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG, Q16653) is a myelin protein expressed on oligodendrocytes. Anti-MOG antibodies recognize a epitopes at P42 and at H103/S104 within the immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain [56]. g Aquaporin-4 isoform M23 (AQP4-M23) is a water channel expressed on astrocytes. Anti-AQP4-M23 antibodies recognize epitopes within loop C (aa146-150) and loop E (aa227-228), but mostly in loop A (aa61-64) [62]. An additional study identified extracellular epitopes within loop A (aa66-69), loop C (N153), and loop E (H230) [65]. Reported intracellular epitopes include aa1-22, aa88-113, and aa252-275 [61]. D69 (red) is vital in maintaining the conformational structure of loop A [63]. Human AQP4-M23 sequence is derived from [210, 211]. Human protein topology, i.e., aa sequences and transmembrane domains (TM), is adapted from UniProt database and UniProt identifiers are shown between brackets. Diagrams do not depict protein crystal structure. Green highlights indicate major (dark green) and minor (light green) epitopes mapped by methods which retain the native in vivo conformational structure of proteins, such as cell-based assays. Orange highlights epitopes determined by methods that denature or linearized proteins, such as western blots and ELISAs (Table 1)
