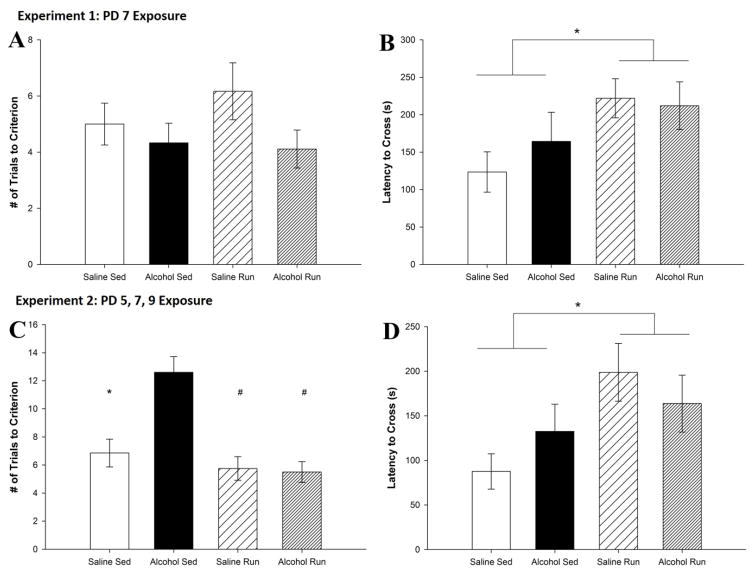
Figure 7. PD 5, 7 and 9 administration but not PD 7 alone impairs Passive avoidance performance.
A. Number of trials to reach criterion on Day 1 for Experiment 1. There were no differences between alcohol-exposed and saline-exposed mice as well as no differences between running and sedentary mice. B. Latency to cross over into the dark chamber on Day 2 for Experiment 1. Exercise significantly increased the latency to cross over for both the alcohol-exposed and the saline exposed-mice. C. Number of trials to learn the Passive avoidance task on Day 1 for Experiment 2. Alcohol exposure significantly increased the number of trials it took to reach criterion for sedentary mice. Running significantly decreased the trials to criterion for alcohol-exposed mice. D. Latency to cross over into the dark chamber on Day 2 for Experiment 2. Exercise significantly increased the latency to cross over in both the alcohol-exposed and the saline-exposed mice. All values represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, #p < 0.001.