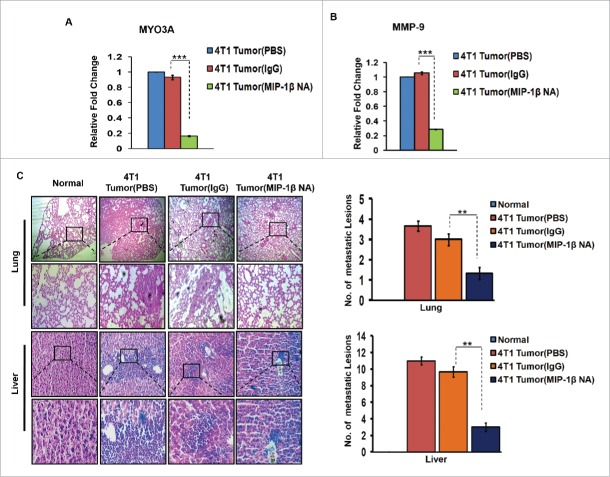
Figure 9.
Diminished expression of MMP-9 and MYO3A upon neutralizing antibody-mediated blockade of MIP-1β function was followed by reduced cellular burden in lungs and diminished presence of metastatic foci in liver of syngenic 4T1/BALB/c mouse model of breast cancer. (A and B) Anti-mouse MIP-1β goat IgG polyclonal antibody-treated 4T1 tumors expressed much lower invasive potential as revealed by significantly downregulated mRNA expression levels of MYO3A. The mRNA expression levels of MMP-9 gene were significantly downregulated. Bars represent Quantitative RT-PCR relative fold change expression ±SE (*p <0.05). (C): On day 26th post grafting, compared to controls (PBS or isotype control antibody (IgG)), the intratumoral administration of MIP-1β-neutralizing antibody (MIP-1β NA) resulted in reduced cellular burden in lungs and perivascular regions of liver from 4T1/BALB/c mouse models. Lung and liver sections obtained from healthy uninoculated mice served as mock control. Bars represent no. of metastatic lesions ±SE (*p < 0.05.). All the experiments were done in triplicates. All the experiments were done in triplicates. Abbreviations—4T1 tumor (PBS): 4T1-induced tumor treated with PBS; 4T1 tumor (IgG): 4T1-induced tumor treated with isotype control antibody; 4T1 Tumor (MIP-1β NA): 4T1-induced tumor treated with MIP-1β-neutralizing antibody.