Figure 1.
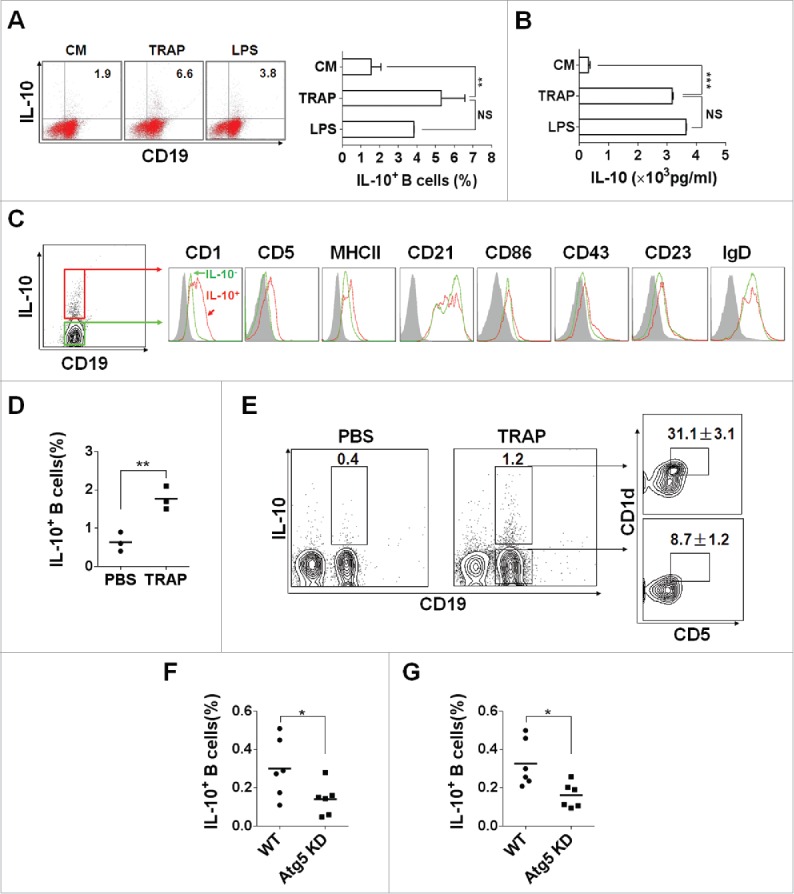
TRAPs induce IL-10-producing B cell differentiation in vitro and in vivo. (A) Frequencies of IL-10-producing B cells determined by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were incubated with TRAPs (3 μg/mL) or LPS (10 μg/mL) for 72 h. PIM stimulation was performed for 5 h before IL-10 staining. (B) ELISA determinations of IL-10 secretion in culture supernatants were also shown. (C) Phenotypic analysis of IL-10+ (red line) or IL-10− (green line) B cells from TRAP-treated B cell cultures for 72 h by flow cytometry. Gray shaded histograms indicate the isotype staining. (D and E) Mice were i.v. injected with TRAPs (30 μg per mouse) three times with 1 d of intervals and frequencies of splenic IL-10+ B cells were determined 4 d after last treatment (n = 3; as shown in D), CD1d and CD5 expression was assessed by flow cytometry as previously shown. Representative contour plot showing CD1d and CD5 expression on IL-10+ and IL-10− B cells, as shown in E. (F and G), Mice bearing established Atg5 KD 4T1 tumor or control 4T1 tumor were sacrificed (n = 6) when solid tumor volumes reached approximately 150 mm2, and the frequency of IL-10+ B cells in the tumor tissue (as shown in F) and the draining lymph node (as shown in G) was detected. Data (mean ± s.e.m) are representative of three independent experiments. NS: p > 0.05, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 by unpaired t-test (A, B, D, F and G).
