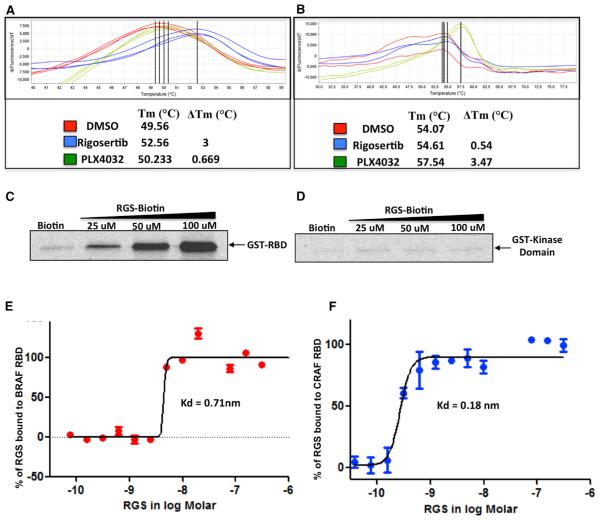
Figure 1. Rigosertib Binds to the RBDs of c-RAF and B-RAF.
(A and B) Recombinant GST-RBD (AA 1–149) of c-RAF (A) or kinase domain (KD) of c-RAF (AA 306–648) (B) were subjected to DSF in the presence of DMSO (control), rigosertib (RGS), or PLX4032 (PLX). GST-RBD and KD reactions were performed in triplicate and duplicate, respectively.
(C) Binding of RGS to GST-RBD. GST-RBD was mixed with total cell lysates and incubated with RGS-biotin conjugate and streptavidin-agarose beads. The precipitates were subjected to western blot analysis using GST-specific antibodies.
(D) GST-KD was mixed with total cell lysates and incubated with RGS-biotin conjugate and streptavidin-agarose beads. The precipitates were processed as described for GST-RBD.
(E and F) Microscale thermophoretic analysis of RGS interaction with c-RAF and B-RAF RBDs. N-terminally labeled recombinant GST-tagged B-RAF and c-RAF RBD proteins were incubated with increasing concentrations of RGS and the binding reactions subjected to MST. RGS binds to the B-RAF and c-RAF RBDs with Kd values of 0.71 nM and 0.18 nM, respectively.
See also Figures S1, S4, and S5.