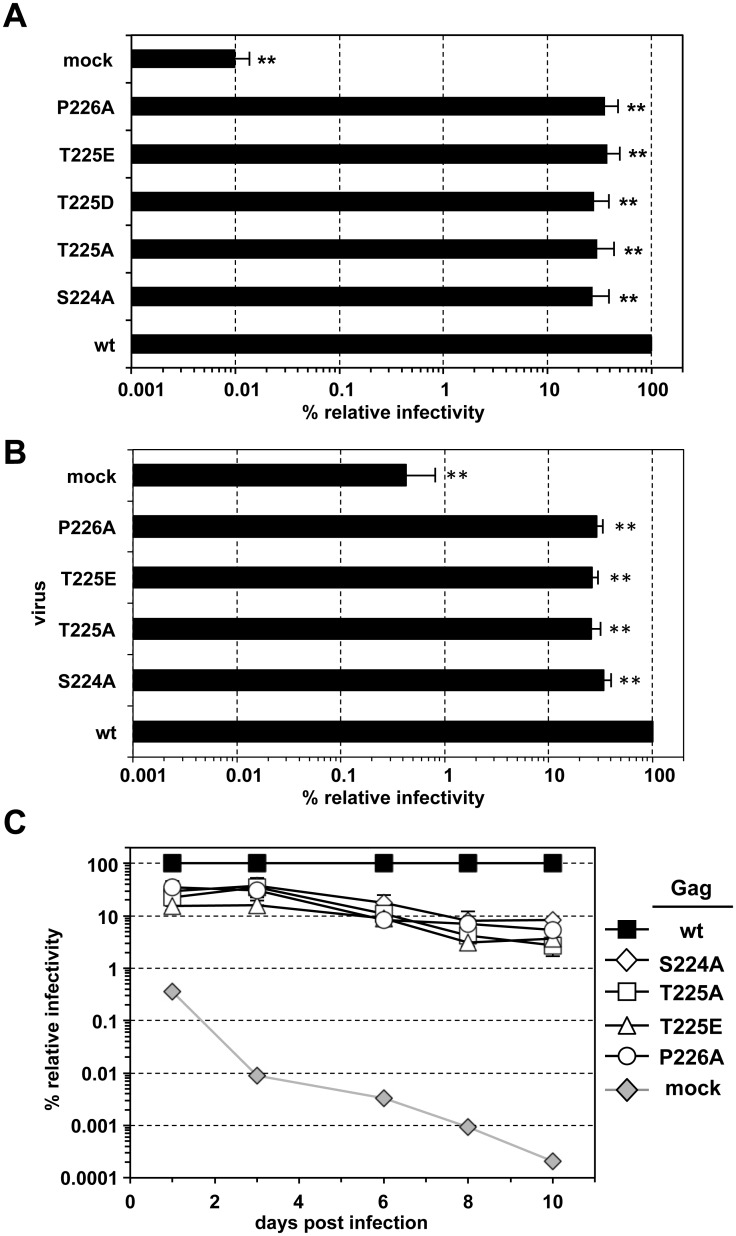
Fig 5. Analysis of PFV wt, iSTP- and pmSTP virions in single-round- and multiple-round infection experiments.
(A) PFV virions were produced by transient transfection of 293T cells with the four-component PFV vector system, containing either the wt Gag or one of the denoted iSTP- and pmSTP Gag variants. Titers of harvested viruses were determined by flow cytometry analysis of infected HT1080 target cells three days post-infection. The mean values and standard deviation for each supernatant were calculated from samples of cells infected with serial virus dilutions as described in Material and Methods. The values obtained using wt PFV Gag expression plasmids were arbitrarily set to 100%. Relative means and standard deviations normalized for Gag content (except mock) from independent experiments (n = 4–9) are shown. Differences between means of wt virus and the individual mutants were analyzed by Welch’s t test (**, p<0.01). Absolute titers of wt supernatants ranged between 1.2 x 106 and 1.2 x 107 eGFP ffu/ml. (B) Replication-competent PFV virions were produced by transient transfection of proviral expression vectors, containing either the wt Gag or one of the denoted iSTP- and pmSTP Gag variants into 293T cells. Viruses were harvested two days post-transfection and used to infect HT1080 PLNE target cells. Titers were determined by flow cytometry analysis one day post-infection. The values obtained using wt PFV Gag expression plasmids were arbitrarily set to 100%. Relative means and standard deviations normalized for Gag content (except mock) from independent experiments (n = 3–8) are shown. Differences between means of wt virus and the individual mutants were analyzed by Welch’s t test (**, p<0.01). Absolute titers of wt supernatants ranged between 1.7 x 104 and 7 x 104 eGFP ffu/ml. (C) Titers of iSTP- and pmSTP mutant PFV particles relative to wt over multiple rounds of target cell infection. Viruses were produced and harvested as described in panel B and Gag content normalized amounts of viral supernatants were used to infect HT1080 PLNE in serial dilutions. At different time points post-infection (as indicated on the x-axis) cells were harvested for flow cytometry analysis to determine viral titers. The values obtained using wt PFV supernatants at each time point were arbitrarily set to 100%. Relative means and standard deviations from two independent experiments are shown.