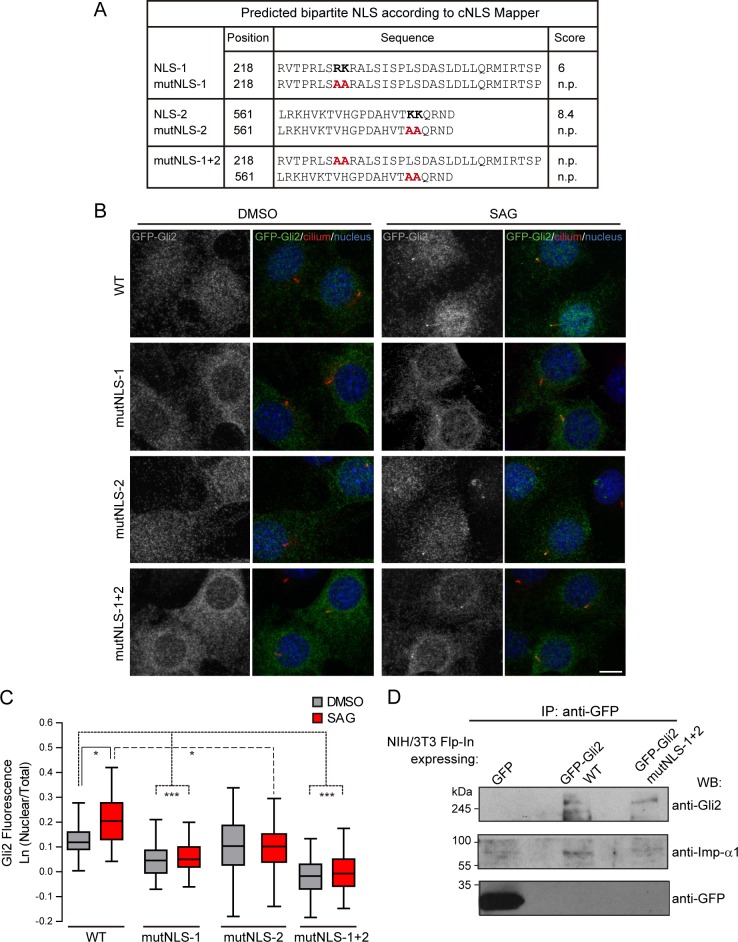
Fig 2. cNLSs are necessary for Gli2 nuclear import.
(A) Sequences in Gli2_Mm predicted as cNLSs by cNLS-Mapper [40] using a cut-off of 5 with the corresponding scores (out of 10). Residues that were mutated for alanines in the mutNLS constructs are in bold. The mutated sequences are not predicted (n.p.) as cNLS. (B) Transduced NIH/3T3 cells expressing GFP-Gli2, wt or cNLS mutants (mutNLS-1, mutNLS-2 or mutNLS-1+2), were treated with SAG for 90 min or DMSO as control. Cells were stained for cilium (anti-Ac.Tub, red), GFP-Gli2 (anti-GFP, green) and nucleus (DAPI, blue). The same pictures are also shown with the channel corresponding to GFP-Gli2 in grey scale to help the visualization. Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) Quantification of nuclear Gli2 was performed as explained in Fig 1C. Black, solid line indicates comparison between control and Hh activated conditions for wtGli2, dotted line indicates comparison between wtGli2 under basal condition and mutNLS-1 or mutNLS-1+2 under basal or activated conditions and black, discontinued line indicates comparison between activated conditions for wtGl2 and mutNLS-2. *p<0.01, *** p<0.0001 (Kruskal-Wallis test). (B) and (C) are representative of four independent experiments and at least 70 cells were analysed for each condition. (D) WB detecting Imp-α1 after precipitating GFP-Gli2 or GFP-Gli2-mutNLS-1+2 with GFP-Trap from NIH/3T3 Flp-In expressing at endogenous levels the constructs mentioned above. Membranes were cut at different levels so as to detect in the same samples the precipitated GFP-Gli2 (using an anti-Gli2 antibody) and GFP (left panels).