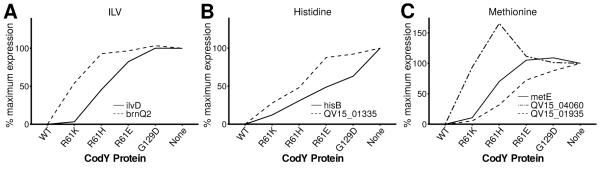
Fig. 2. S. aureus prioritizes amino acid uptake in response to reductions in CodY activity.
All data here and in subsequent figures are presented as the means of at least two independent experiments. RNA-Seq data are shown; % maximal expression relative to the codY null mutant (SRB372, None) is plotted across strains producing varying amounts of CodY regulatory activity: CodYWT, SRB337; CodYR61K, SRB506; CodYR61H, SRB623; CodYR61E, SRB577; CodYG129D, SRB493. In each panel, genes for nutrient transport are more sensitive to changes in CodY activity and reach 100% prior to genes for nutrient biosynthesis. A. CodY-repressed genes coding for the uptake (brnQ2, QV15_01265) and synthesis (ilvD) of ILV. B. CodY-repressed genes coding for the uptake (proposed histidine transporter, QV15_01335) and synthesis (hisB) of histidine. C. CodY-repressed genes coding for the uptake (metNIQ1 [QV15_01935-01945], metNIQ2 [QV15_04055-04065]) and synthesis (metE) of methionine.