FIGURE 3:
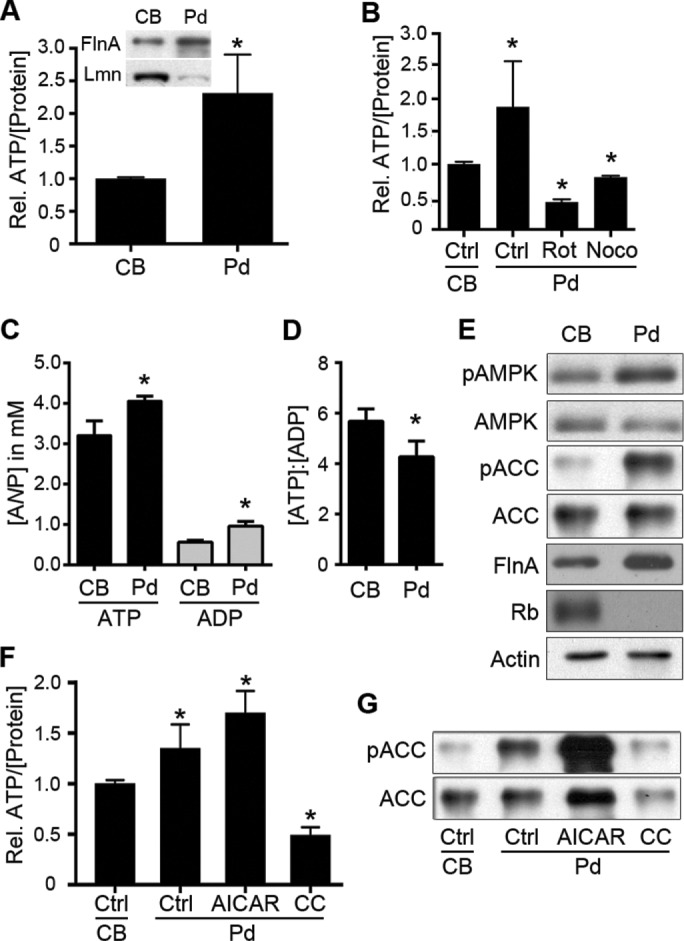
Pseudopodia harbor altered nucleotide levels, ATP/ADP ratio, and AMPK activity compared with cell bodies. (A) Relative levels of ATP (per microgram of protein) were assayed from equal amounts of extracts from purified cell bodies (CBs) and pseudopodia (Pd; n = 4, *p < 0.001). Inset, enrichment of CB and Pd fractions was confirmed by immunoblotting for the leading edge marker filamin A (FlnA) and the nuclear marker lamin A/C (Lmn) in purified Pd and CBs, respectively. (B) Relative ATP levels in Pd relative to respective cell bodies were determined in control conditions (Ctrl; p < 0.05) or after treatment of Pd with rotenone (Rot, 2.5 μM; p < 0.001) or nocodazole (Noco, 0.1 nM; p < 0.01) for 20 min (n = 3 for all samples). (C) Actual ATP and ADP concentrations in Pd relative to respective cell bodies. ATP and ADP concentrations in CB and Pd extracts were determined and used, along with averaged measurements of CB and Pd volumes, to determine true subcellular nucleotide concentrations (average ± SD from three experiments, nCB = 6 and nPd = 15; p = 0.017 and 0.0052 for ATP and ADP, respectively). (D) Average ATP-to-ADP ratio (± SD) in CB and Pd determined from the data in C (p = 0.0365). (E) CB and Pd extracts were immunoblotted to assess levels of active, phospho-T172 AMPK (pAMPK) and AMPK-phosphorylated ACC (pACC), as well as total AMPK and ACC, as indicated. Filamin A (FlnA), retinoblastoma protein (Rb), and actin were immunoblotted to show pseudopod enrichment, cell body enrichment, and equal protein loading, respectively. (F) Relative levels of ATP in Pd relative to cell bodies determined in control conditions (Ctrl; p < 0.005) or after treatment of Pd with AICAR (0.5 mM; p < 0.001) or compound C (CC; 10 μM; p < 0.001; n = 4 for all samples). (G) Extracts from control-treated CBs, control-treated Pd (Ctrl) or Pd treated with AICAR or compound C (CC) as in F were immunoblotted to assess levels of AMPK-phosphorylated or total ACC, as indicated.
