FIGURE 4:
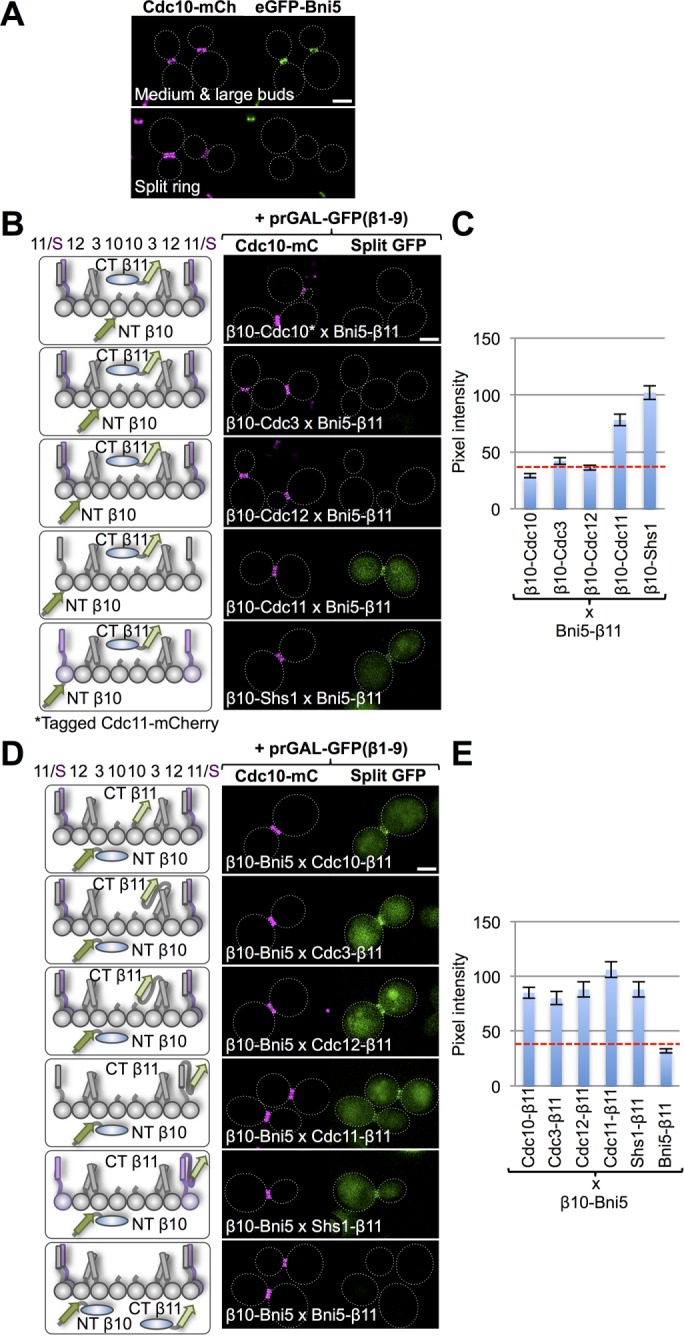
Interaction of Bni5 with the septin collar. (A) Cells (strain GFY-1318) expressing an eGFP-Bni5 fusion and coexpressing Cdc10-mCh were grown to mid exponential phase and visualized by fluorescence microscopy. Representative cells with a medium-to-large bud and an intact septin collar before cytokinesis (top) or with a split septin collar diagnostic of cells in cytokinesis (bottom). Dotted white line, cell periphery; scale bar, 2 μm. (B) Diploids (127, 120, 141, 134, and 148) expressing Bni5-(linker)33-β11 and N-terminally β10-(linker)18–tagged versions of the five mitotic septins (left) visualized by fluorescence microscopy as in Figure 1B (right). For the strain expressing β10-(linker)18-Cdc10 (top), the fiducial mark for the septin collar was Cdc11-mCh and, for all of the others, Cdc10-mCh. (C) Quantification, as in Figure 1C, of the data in B. (D) Diploids (151, 150, 153, 152, and 154) expressing β10-(linker)18-Bni5 and C-terminally (linker)33-β11–tagged versions of the five mitotic septins (left) visualized by fluorescence microscopy as in Figure 1B (right). Bottom, homotypic Bni5 interaction was assessed by examining a diploid (155) coexpressing Bni5-(linker)33-β11 and β10-(linker)18-Bni5. (E) Quantification, as in Figure 1C, of the data in D.
