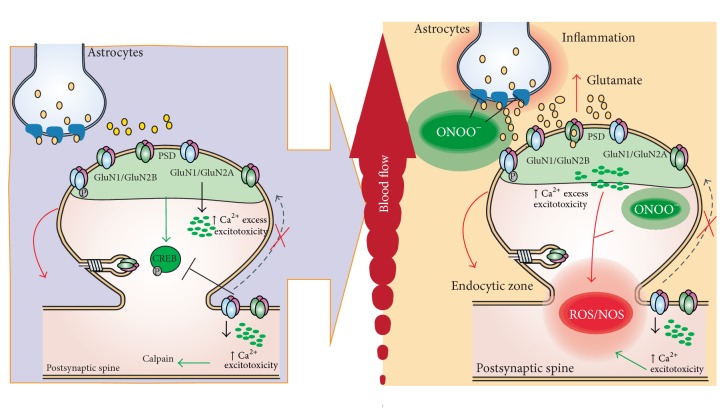
Figure 1.
Implications of NMDAR in acute damage, ischemia/reperfusion. During ischemia, the overactivation of STEP induces the internalization of NMDARs, principally of GluN2B subunits, and the activation of extrasynaptic NMDAR triggers an excess of Ca2+ influx and excitotoxic events related to decreases in CREB activation and increases in calpain activity. During reperfusion, injury induces the generation of ROS and ONOO−. The increase of ONOO− alters the activity of glutamate transporter in astrocytes. The excess glutamate leads to the overactivation of NMDARs.