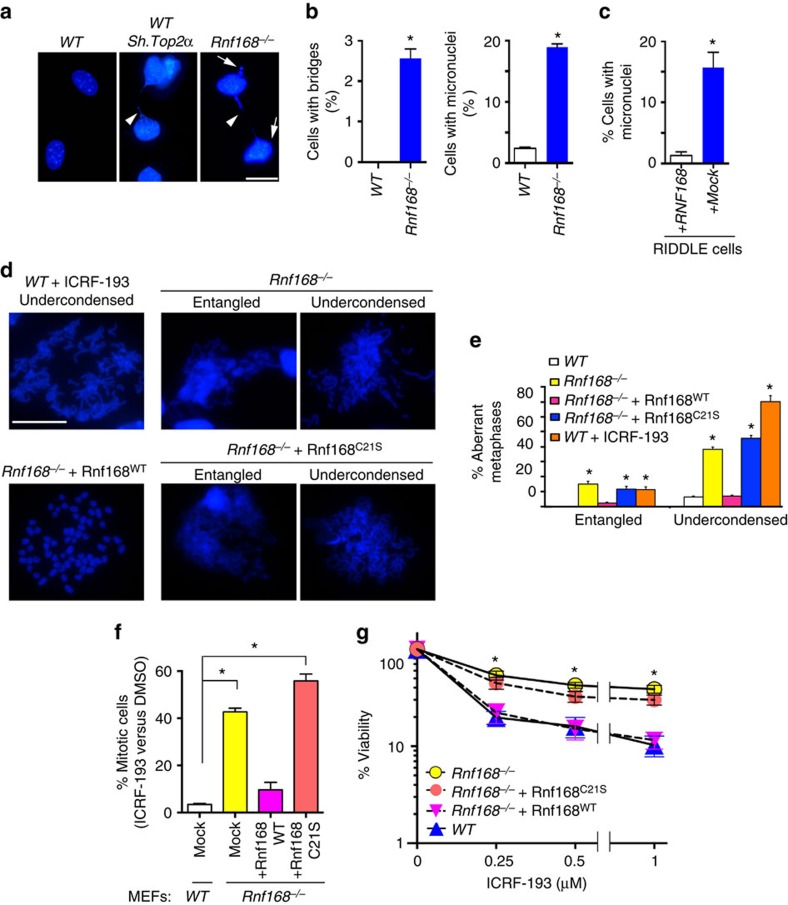
Figure 5. Deficiency of the E3 ligase RNF168 impairs chromosome segregation and promotes chromosome entanglement and under-condensation.
(a) WT and Rnf168−/− MEFs, and Top2α knockdown control MEFs were fixed and stained with DAPI. Representative cells with defective chromosome segregation, as indicated by chromosome bridges (arrow head) and micronuclei (arrow) are shown. (b) Histograms show quantification of cells with chromosome bridges or micronuclei (mean±s.e.m., n=3). *P<0.05. (c) Histograms show the fraction of RIDDLE cells reconstituted with HA-RNF168 or HA-empty vector that display micronuclei (mean±s.e.m., n=3). *P<0.05. (d; upper panels) Representative metaphase spreads showing undercondensed chromosomes in WT MEFs 24 h post ICRF-193 treatment (positive control), and in Rnf168−/− DMSO-treated MEFs. (d, lower panels) Representative metaphase spreads of DMSO-treated Rnf168−/− MEFs complemented with RNF168-WT (WT) or the E3 ligase deficient RNF168-C21S (C21S). (e) Histograms show quantification of abnormal metaphase spreads with entangled or undercondensed chromosomes from the indicated cells (mean±s.e.m., n=3). *P<0.05 compared with WT MEFs. (f) Histograms present the mean fraction of MEFs evading ICRF-193-induced G2 arrest as compared with DMSO-treated controls (mean±s.e.m., n=3). Data are shown for WT MEFs, mock infected Rnf168−/− MEFs and Rnf168−/− MEFs complemented with RNF168-WT or RNF168-C21S. 3T3 MEFs were used for these experiments. Data shown are for 6 h post-treatment with colcemid±4 μM ICRF-193. *P<0.05 compared with WT MEFs. (g) Clonogenic assay was used to determine sensitivity to ICRF-193 of mock infected WT and Rnf168−/− MEFs, as well as Rnf168−/− MEFs complemented with RNF168 (WT or C21S mutant). Data are presented as the mean±s.e.m. (n=4). *P<0.05 compared with WT MEFs. Scale bar, 20 μm.