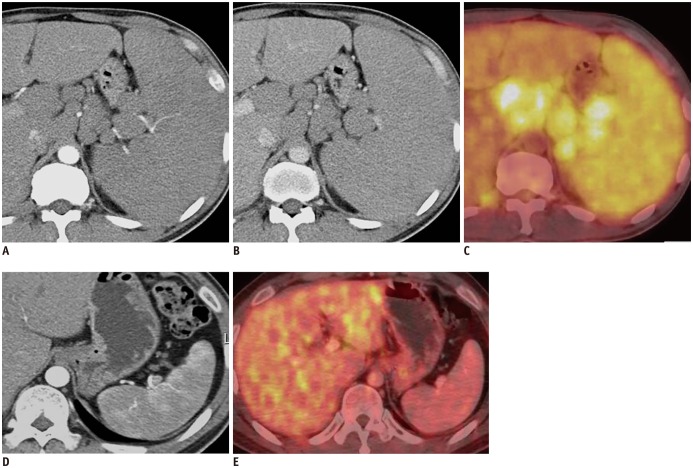
Fig. 1. 41-year-old man with mantle cell lymphoma.
Axial contrast-enhanced MDCT shows marked splenomegaly, multiple lymphadenopathies and obliteration of normal heterogeneous enhancement of spleen on AP image (A) and homogeneous enhancement on PVP image (B). PET/CT shows diffusely increased FDG uptake in spleen and multiple enlarged lymph nodes, suggesting lymphoma involvement (C). After chemotherapy, axial contrast-enhanced MDCT shows restoration of normal heterogeneous enhancement of spleen and interval marked decrease in size of enlarged spleen on AP image (D). Follow-up PET/CT after chemotherapy shows normal splenic uptake less than hepatic uptake (E). AP = arterial phase, FDG = fluorodeoxyglucose, MDCT = multidetector CT, PET/CT = positron emission tomography/CT, PVP = portal venous phase