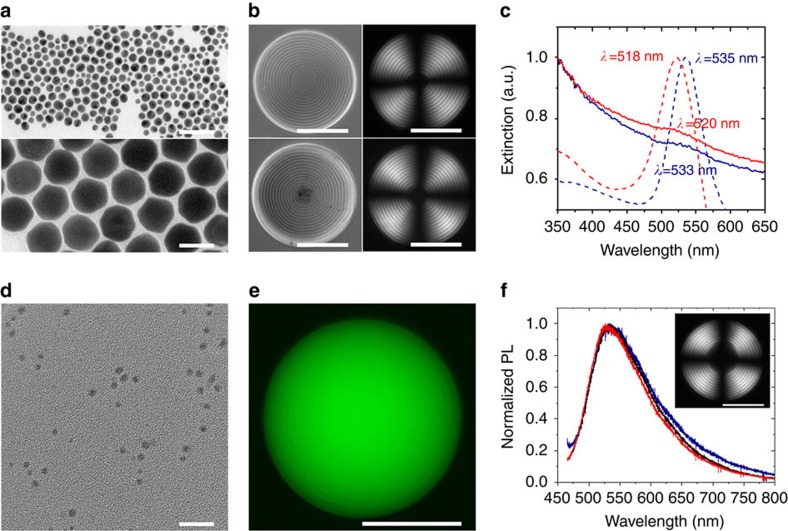
Figure 7. Co-assembly of CNCs and inorganic nanoparticles.
(a) TEM images of 10 nm (top) and 50 nm (bottom) gold NPs. The scale bar is 50 nm. (b) BF (left panel) and POM (right panel) images of the Ch-CNC droplets loaded with 10 nm gold NPs (top panel) and 50 nm gold NPs (bottom panel). The concentration of gold NPs in the droplets is 0.1 mg ml−1. The scale bar is 50 μm. (c) Extinction spectra of aqueous gold NP dispersion (dashed lines) and Ch-CNC droplets (solid lines) loaded with 10 nm (red lines) and 50 nm (blue lines) gold NPs. The broadening of extinction spectra of the NP-loaded droplets was caused by the light scattering by droplets in the visible light region. (d) TEM images of carbon dots. The scale bar is 20 nm. (e) FM image of the Ch-CNC droplet carrying carbon dots at concentration of 1 mg ml−1. The scale bar is 50 μm. (f) Photoluminescence spectra of the core (black line) and shell (red line) of the Ch-CNC droplets loaded with carbon dots, and an aqueous dispersion of carbon dots (blue line), both excited at λexc=440 nm. Inset: POM image of the droplet loaded with carbon dots. The scale bar is 50 μm. φ0=0.043 in b–f.