Figure 1. INPP5E is essential in neurons for autophagosome–lysosome fusion.
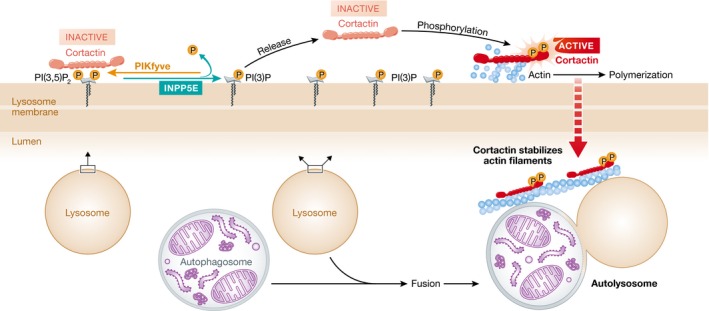
INPP5E partially localizes on lysosomes where it converts PI(3,5)P2 to PI(3)P. Cortactin can directly bind PI(3,5)P2, and INPP5E decreases PI(3,5)P2 levels to potentially release cortactin. Released cortactin then can be phosphorylated by kinases to become activated. Activated cortactin functions to promote actin polymerization and to maintain the stability of actin filaments on lysosomes. Hasegawa et al (2016) suggest that decreased actin filament abundance due to PI(3,5)P2‐bound cortactin is responsible for the compromised autophagosome–lysosome fusion observed in INPP5E‐deficient and disease‐associated mutant‐expressing neuronal cells.
